Among the different types of servo motors available, the 3-phase servo motor and 2-phase servo motor are commonly used. Although they both have the same function, their efficiency, applications, performance, and design are different. We will compare 3-phase and 2-phase servo motors in detail, analyzing their differences, advantages, and disadvantages.

Understanding Servo Motors
Before diving into the specifics of 2-phase and 3-phase servo motors, let’s first understand the general concept of a servo motor.
One type of electric motor designed to accurately rotate or move to a preset point is called a servo motor. It is comprised of a motor and a sensor that gives the controller information about the motor’s location and speed, which the controller uses to modify the motor’s behavior. Servo motors can be broadly classified into two categories based on the number of phases they use: single-phase and three-phase motors.
- Single-phase Servo motor: These motors operate on single-phase alternating current (AC) and are typically used for low-power applications.
- Three-phase Servo motor: These motors operate on three-phase AC power, providing higher efficiency and torque, making them suitable for high-power and high-precision applications.
In this article, we will focus on the 2-phase and 3-phase variants of AC servo motors, which are commonly used in industrial automation and motion control systems.
3 Phase Servo Motors
A 3-phase servo motor is designed to operate using a three-phase AC power supply, which provides three distinct electrical signals that are offset by 120 degrees. This configuration helps produce a smoother and more continuous rotation, making 3-phase motors ideal for high-performance applications requiring high torque and precision.
Key Characteristics of 3-Phase Servo Motors:
- Power Supply: The motor operates on three-phase alternating current (AC), with three distinct electrical phases, making it suitable for high-power applications.
- Torque and Efficiency: The continuous flow of power through the three phases results in smoother torque delivery, reducing vibrations and improving the motor’s efficiency.
- Performance: A 3-phase motor generally provides higher torque, better speed regulation, and more efficient operation compared to a 2-phase motor.
Advantages of 3-Phase Servo Motors:
- Higher Efficiency: Because of their constant power supply, 3-phase motors are more efficient, using less energy and producing less heat.
- Improved Torque and Speed Control: With a constant power flow, the 3-phase servo motor can maintain better torque and speed regulation, making it suitable for high-precision applications.
- Reduced Motor Vibration: The smooth transition between phases helps in reducing vibrations, leading to quieter operation and longer motor life.
Applications of 3-Phase Servo Motors:
- Robotics: For precise motion control.
- CNC Machines: In both milling and lathe machines.
- Conveyor Systems: For controlling belt speed and positioning.
- Elevators and Escalators: For precise speed regulation.
- Electric Vehicles: For efficient motor control in traction systems.
2-Phase Servo Motors
A 2-phase servo motor, on the other hand, operates using a two-phase AC supply. The two phases are 90 degrees apart, and the motor’s control system adjusts the current in these phases to provide the necessary movement.
Key Characteristics of 2-Phase Servo Motors:
- Power Supply: 2-phase motors use a two-phase AC power supply, which is less common than the standard 3-phase supply.
- Torque and Performance: While the torque delivered by a 2-phase motor is generally lower than that of a 3-phase motor, it is still suitable for applications requiring moderate precision and control.
- Cost-Effective: Due to the simpler design, 2-phase motors are often more affordable, which makes them appealing for budget-conscious applications.
Advantages of 2-Phase Servo Motors:
- Cost-Effective: 2-phase motors tend to be less expensive than 3-phase motors due to the simpler electrical design and fewer components.
- Simpler Control Systems: The motor control systems for 2-phase motors are generally simpler and more affordable, making them a good choice for basic applications.
- Compact Design: Typically, 2-phase motors are more compact and lightweight compared to 3-phase motors, which may make them suitable for applications with limited space.
Applications of 2-Phase Servo Motors:
- Small-Scale Robotics: For simple, less demanding movements.
- Medical Equipment: In applications where precision is needed, but the power demands are low.
- Small Automation Systems: Such as conveyor belts or position control for less complex systems.
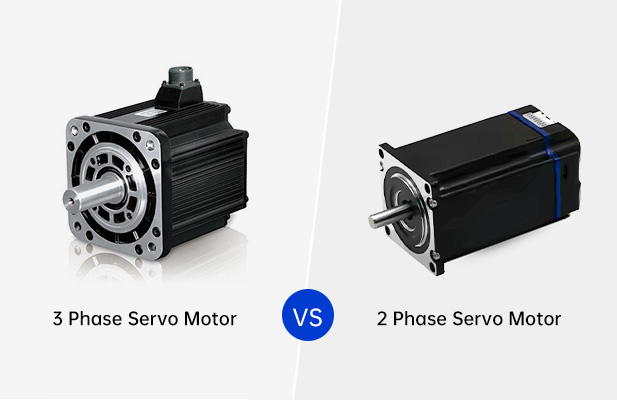
Key Differences Between 3-Phase and 2-Phase Servo Motors
Power and Efficiency:
- 3-Phase Servo Motors: They are more effective at controlling torque and speed because they use three-phase power, which provides a constant power supply.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: Operate with only two phases, which limits their efficiency compared to 3-phase motors. While they are still efficient for low-to-medium power applications, they cannot match the power density and smoothness of a 3-phase system.
Torque Delivery and Smoothness:
- 3-Phase Servo Motors: These motors deliver smoother torque because the power is divided over three phases, providing constant rotation without noticeable power drops. The continuous current flow also results in less vibration.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: The torque delivery is not as smooth as 3-phase motors. Since the power is divided over only two phases, the motor experiences more fluctuations in torque, which can lead to increased vibration and noise in operation.
Cost and Complexity:
- 3-Phase Servo Motors: More complex in design and require a 3-phase power supply, which can make the system costlier both in terms of initial investment and operational costs.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: Typically simpler and cheaper, both in terms of hardware and control systems. They might need more upkeep, though, and they might not be appropriate for activities requiring a lot of power and precision.
Size and Weight:
- 3-Phase Servo Motors: Generally larger and heavier due to the additional components required for handling three phases of power.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: Because they are lighter and more compact, they can be used in situations where weight is an important consideration or where space is at a premium.
Applications:
- 3-Phase Servo Motors: Best suited for applications requiring high precision, continuous power, and high efficiency, such as robotics, CNC machines, and high-end industrial automation systems.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: More suitable for simpler, low-power applications where budget and size constraints are more important than maximum precision or torque.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison Chart
Here’s a side-by-side comparison chart highlighting the efficiency and performance differences between 3-phase and 2-phase servo motors.
| Feature | 3-Phase Servo Motor | 2-Phase Servo Motor |
| Power Supply | Three-phase AC power | Two-phase AC power |
| Efficiency | High efficiency, continuous torque delivery | Moderate efficiency, less smooth operation |
| Torque Delivery | Smooth and continuous torque | Fluctuates more, less smooth operation |
| Control Complexity | More complex control system | Simpler control system |
| Cost | More expensive due to higher complexity | Lower cost, cost-effective |
| Applications | High-precision, high-power systems (CNC, robotics) | Low-power, cost-sensitive applications |
| Size & Weight | Larger and heavier | Compact and lightweight |
How to Choose Between 3-Phase and 2-Phase Servo Motors?
Choosing between a 3-phase and a 2-phase servo motor depends on a variety of factors, including your application requirements, performance needs, cost constraints, and space limitations. Here is a detailed guide to assist you in making an informed choice:

Evaluate Power Requirements
- 3-Phase Servo Motors: Applications requiring constant, high torque and efficiency are best suited for them. This makes them perfect for industrial automation, robotics, CNC machines, and electric vehicles where large amounts of power need to be delivered smoothly and consistently.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: These motors typically handle lower power requirements compared to their 3-phase counterparts. If your system doesn’t require a large amount of power or continuous high-torque output, a 2-phase servo motor can be a more economical choice. It is well-suited for applications like small-scale robotics, simple automation systems, or other applications with low-to-moderate power demands.
Decision Tip:
If you’re working with high power and high-torque applications (like industrial machines, large robots, or conveyor systems), a 3-phase motor is the better choice. For smaller, less demanding systems, a 2-phase motor will suffice.
Consider Precision and Control Needs
- 3-Phase Servo Motors: These motors excel in precise speed regulation, smooth torque delivery, and accurate position control due to their continuous power supply across three phases. A 3-phase motor is frequently the ideal option if your application calls for a high degree of precision, like in CNC machines, robotic arms, or medical equipment.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: While 2-phase motors provide good control for less complex systems, they do not offer the same level of smoothness or precision as 3-phase motors. The torque delivery is not as continuous, leading to more fluctuations. Therefore, 2-phase motors are suitable for applications where high precision isn’t a priority but moderate control is still required.
Decision Tip:
If your application demands high precision and smooth control, such as automated assembly lines or robotic systems with intricate movements, a 3-phase motor is recommended. For simpler applications, such as conveyor belts or basic automation systems, a 2-phase motor will be adequate.
Assess Cost and Budget Constraints
- 3-Phase Servo Motors: These motors are generally more expensive due to their complexity, advanced control systems, and higher power capabilities.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: Since they are simpler in design and use fewer components, 2-phase motors are usually more affordable. They are a cost-effective choice for applications with low-to-medium power needs and where the motor’s precision and torque requirements are not as critical.
Decision Tip:
If cost-effectiveness is a primary concern and your application doesn’t require high power or precision, a 2-phase motor is the way to go. However, if your project requires long-term reliability and operational efficiency, investing in a 3-phase motor will pay off in the future.
Space and Size Limitations
- 3-phase servo motors are often heavier and bulkier than two-phase motors. The additional parts needed to manage three power phases are the cause of this. An effective option for applications where weight and space are not crucial is a three-phase motor.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: 2-phase motors are typically more compact and lighter, which makes them ideal for applications where space is limited or where weight is a concern. Because of their simplified design, they are also simpler to install and maintain.
Decision Tip:
If your system has limited space or needs to keep weight to a minimum (such as mobile robots or small machines), a 2-phase motor is a better fit. If space and weight are not a significant issue, a 3-phase motor can still be considered.
Evaluate Power Supply Availability
- 3-Phase Servo Motors: These motors require a 3-phase power supply. In industrial situations where three-phase electricity is readily available, this is not a problem. However, if your application is in a location where only single-phase power is available, you may need to use a converter or opt for a 2-phase motor.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: 2-phase motors operate on a simpler two-phase power supply, which is more common in smaller applications or areas with limited access to three-phase power. If you’re working in environments where only two-phase power is available, this motor might be a more convenient choice.
Decision Tip:
If your facility already has a 3-phase power supply, a 3-phase motor is ideal. However, if you need to use a two-phase power supply, a 2-phase motor might be more suitable, although it may not offer the same efficiency and performance as a 3-phase motor.
Maintenance and Reliability
- 3-Phase Servo Motors: These motors are typically more durable and long-lasting due to their continuous power flow and smoother operation. They require less frequent maintenance and typically offer higher reliability in demanding environments. However, their complexity may require more technical expertise for repairs and adjustments.
- 2-Phase Servo Motors: While simpler in design, 2-phase motors tend to be more prone to wear and tear due to the more variable torque delivery. They may also require more frequent maintenance if used in demanding applications, but they are often easier to repair due to their simpler control systems.
Decision Tip:
If your application requires high reliability and minimal downtime, a 3-phase motor is the better choice. For less demanding applications where maintenance is easier to handle, a 2-phase motor may be sufficient.
If you need a reliable, long-lasting motor for demanding tasks, a 3-phase servo motor is likely your best option. A reputable servo motor manufacturer can provide the necessary expertise and quality for such high-performance applications. However, for budget-friendly, lower-power applications, a 2-phase servo motor can offer significant savings while still providing adequate performance.