Micro Stepper Motor Manufacturer
We design and produce small and miniature custom stepper motors in a variety of sizes and power options, divided into PM stepper motors and hybrid stepper motors, voltage ranging from 5v-24v. Our high torque stepper motor is suitable for various high-precision industrial applications.
To ensure our motors precisely meet your requirements, we offer a variety of customizable options:
- Step Angle: 1.8°, 0.9°, 7.5°and more.
- Size and Form Factor: Custom sizes to fit your mechanical design constraints.
- Number of Phases: 2-phase, 3-phase, and 5-phase options and more.
- Shaft Modifications: Custom shaft lengths and diameters.
- Special Features: Explosion proof , waterproofing and silent.
Home / Stepper Motor
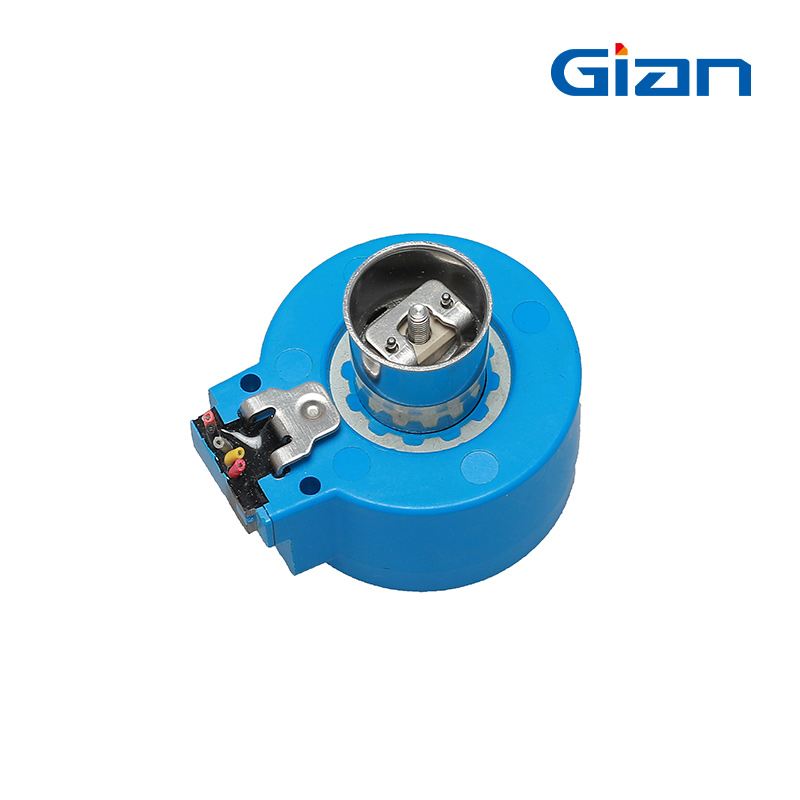
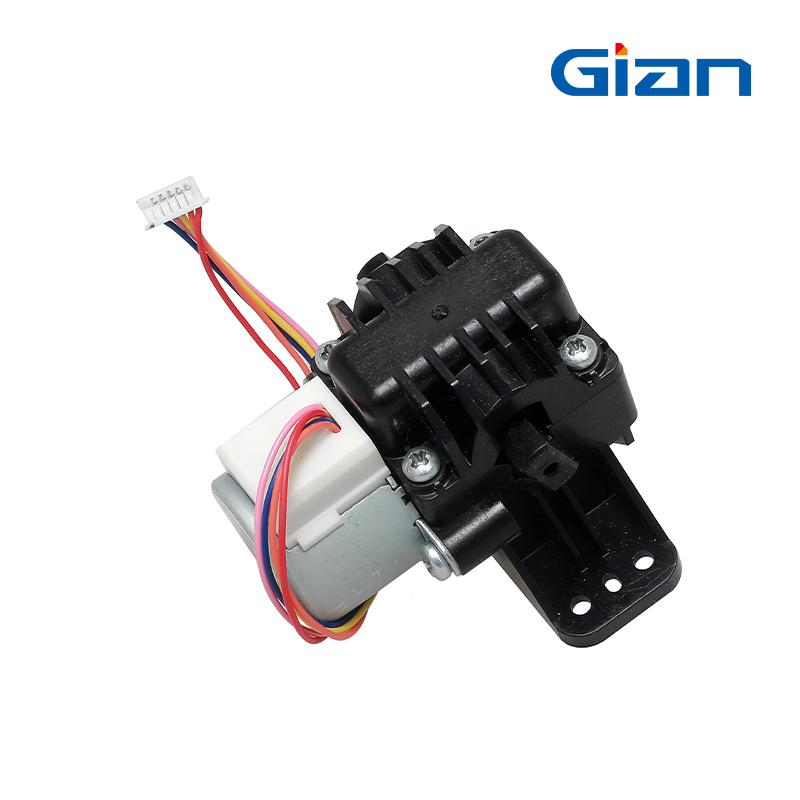
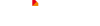
stepper motor Component
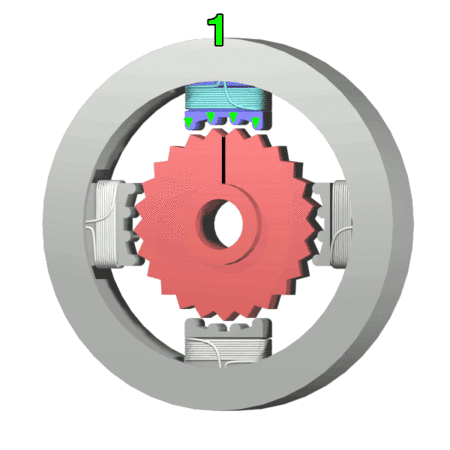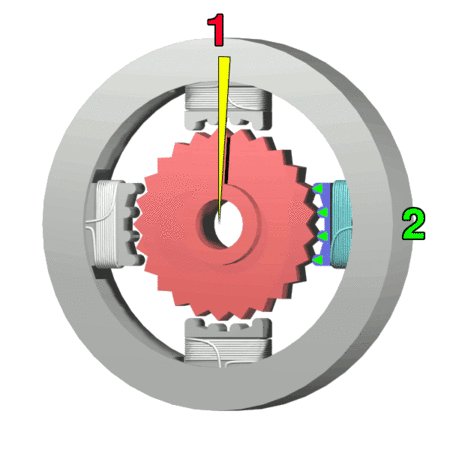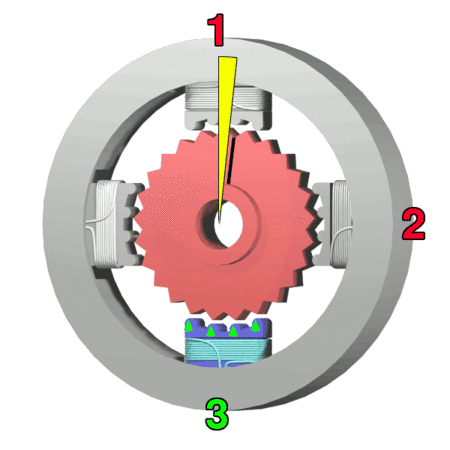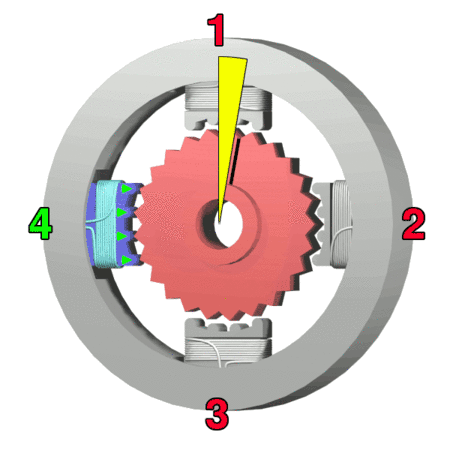
- Rotor: The rotating component of the motor typically comprises permanent magnets or soft iron.
- Stator: The stationary part of the motor has windings that generate the magnetic field.
- Windings: Wire coils within the stator produce magnetic fields when energized.
- Bearings: Stabilize the rotating shaft, reduce friction, and ensure smooth, precise motion.
- Shaft: The component that extends from the rotor and transfers mechanical power to the load.
- End Bells: End covers that house the bearings and provide structural support.
- Housing: The outer casing that encases and protects the internal components.
- Lead Wires: Electrical connections for supplying power to the stator windings.
By Type
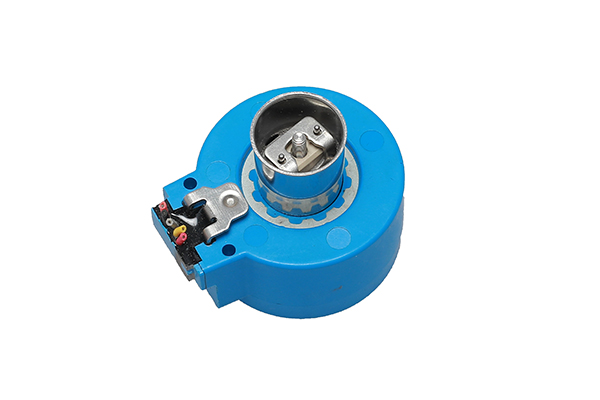

Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor
- Rotor Composition: Permanent magnets.
- Step Angle: Typically 3.75° to 18° per step.
- Torque: Lower torque compared to hybrid stepper motors.
- Resolution: Lower resolution due to larger step angles.
- Applications: Printers and small automation devices.
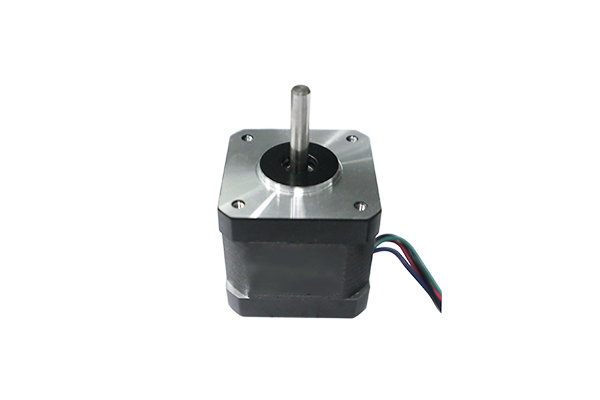

Hybrid Stepper Motor
- Rotor Composition: A combination of PM and soft iron.
- Step Angle: Typically 0.9° to 1.8° per step.
- Torque: Higher torque due to better magnetic coupling.
- Resolution: Higher resolution due to smaller step angles.
- Applications: CNC machines, robotics, and industrial automation.
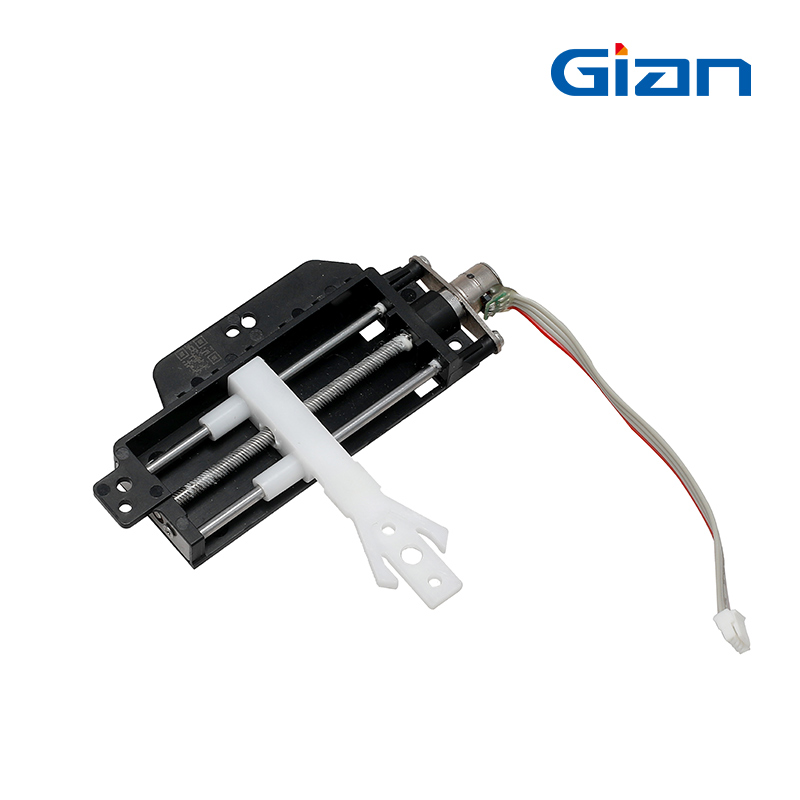
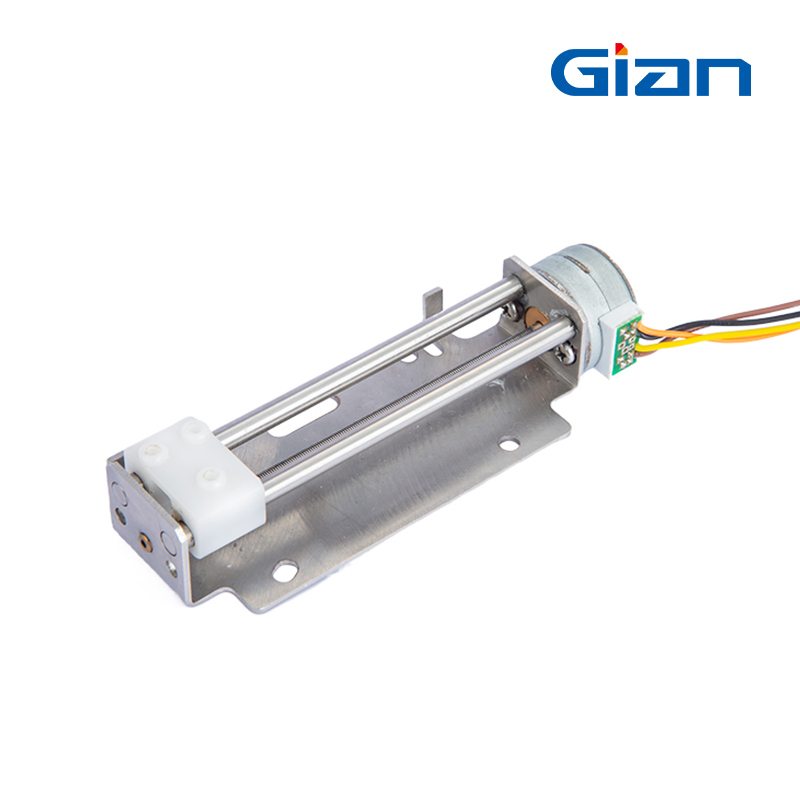
Linear Stepper Motor
- Rotor Composition: Permanent magnet or variable reluctance.
- Step Angle: Small step increments.
- Torque: Consistent linear force.
- Resolution: High resolution with fine step sizes for precise positioning.
- Applications: CNC machines, 3D printers, robotics.
By Shaft Type
Our stepper motor shaft types include dual shaft, double shaft, and hollow shaft. If you have any needs, please contact us!
Dual Shaft
- Dual shaft stepper motor has two shafts extending from opposite ends, enabling independent or simultaneous connection of mechanical components on each shaft.
- Used where multiple outputs or components need coupling on both ends.
Hollow Shaft
- Hollow shaft stepper motor accommodates wires, shafts, or other mechanisms through its center, facilitating internal component integration and minimizing external clutter.
- Common in robotics and automation for space-saving and organized wiring applications.
Double Shaft
- Often used interchangeably with dual shaft or double shaft motors, these feature two shafts for versatile coupling of components or mechanisms.
- Ideal for synchronous movement or applications needing two outputs from one motor.
By Phase
Our stepper motors have 2 phase, 3 phase and 4 phase and 5 phase options, If you want to customize, please contact us!
2 Phase
- 2 Phase Stepper Motor consists of two windings or phases, typically arranged 90 degrees apart.
- Moderate step resolution; in full-step mode, typically 1.8° each step or 200 steps every rotation.
- Simple control circuit.
3 Phase
- 3 Phase Stepper Motor consists of three windings or phases, arranged 120 degrees apart.
- Higher step resolution than 2-phase motors.
- Requires a more complex driver circuit.
4 Phase
- 4 phase stepper motor consists of four windings or phases and used in unipolar stepper motors.
- Moderate resolution.
- Simple control, especially in unipolar configuration.
5 Phase
- 5 phase stepper motor consists of five windings or phases, arranged 72° apart.
- High step resolution, in full-step mode, this is typically 0.72° every step (500 steps per revolution).
- Requires the most complex driver circuit among the stepper motor types.
By wire
Our stepper motor wires include unipolar(3,5wire), bipolar( 4 wire), 6 wire, and 8 wire configurations.If you want to customize, please contact us!
3 Wire
- 3 wire stepper motor specializes in some small unipolar motors or special configurations.
- Requires a specific driver compatible with 3-wire configuration.
4 Wire
- Standard for bipolar operation.
- 4 wire stepper motor requires h-bridge drivers, limited to bipolar mode.
5 Wire
- Standard for unipolar operation.
- 5 wire stepper motor has simplified control, limited to unipolar mode.
6 Wire
- Stepper with six wires a motor can run in both bipolar and unipolar modes.
- Can be wired for unipolar (using center taps) or bipolar operation (ignoring center taps).
8 Wire
- 8 wire stepper motor is configurable for series, parallel, unipolar, or bipolar.
- Maximum flexibility in wiring and control options.
By Polarity
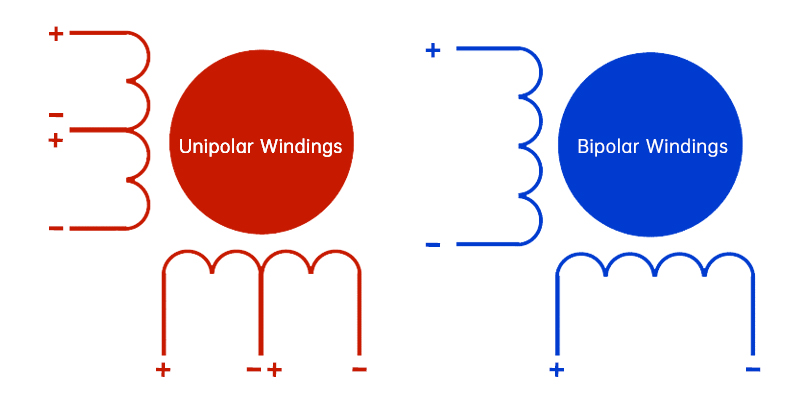
Bipolar
- The bipolar stepper motor has two coils (phases) with a single winding per phase and no center taps.
- Requires a complex driver circuit, often an H-bridge driver, to reverse the current through the coils.
Unipolar
- Unipolar stepper motor has two center-tapped coils, four windings, simpler circuitry for driving.
- Requires a simpler driver circuit, typically with a single transistor per winding.
By control system
Open-Loop
- No Feedback: Open-loop stepper motor operates without feedback, assuming the motor follows a predefined pulse sequence accurately.
- Control: Simple control scheme where the motor's position is determined by the number of input pulses.
Closed-Loop
- Feedback Mechanism: Closed-loop stepper motor uses sensors to monitor the motor's location, speed, and sometimes torque continuously.
- Control: Complex control system adjusts motor operation in real-time, ensuring precise position & speed.
Encoder Feedback
- Feedback Mechanism: Encoder stepper motor uses an encoder on the motor shaft to convert motion into electrical signals, providing precise position feedback.
- Control: The control involves using feedback from the encoder to adjust the motor's operation in real-time.
From 0 to N - Full Motor Solutions
Applications
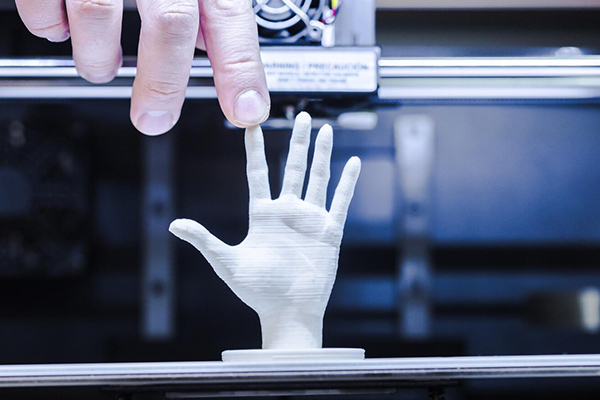

3D Printers
The precise control of the print head and bed movement by the 3D printer stepper motor enables high accuracy in layer deposition, resulting in detailed 3D prints.
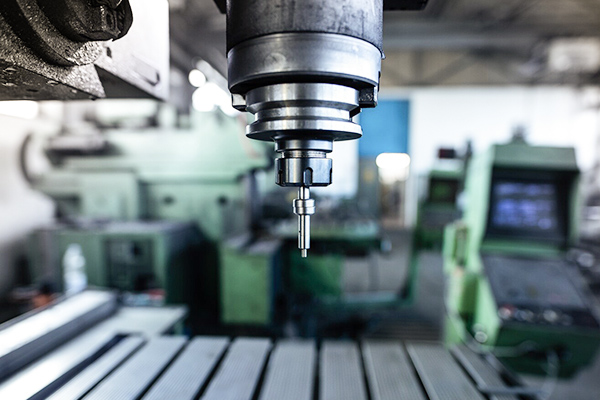

CNC Machines
The movement of cutting tools and workpieces by the CNC stepper motor provides high precision and repeatability for complex machining tasks.

Robots
The joint and arm movement by the robot stepper motor in robotic systems allows for accurate positioning and smooth operation in automated tasks.

Industrial Equipment
The control of conveyor belts, actuators, and automated machinery by the industrial stepper motor ensures reliable and precise operation in industrial automation.

Cars
The control of headlight positioning, climate control vents, and infotainment systems by the car stepper motor enhances functionality and user experience with precise adjustments.

CD Drives
The positioning of the laser read/write head by the CD drive stepper motor provides precise control for accurate data reading and writing.