AC Servo Motor Manufacturer
Our brushless and brushed small AC servomotors are flexible, application-oriented and meet the most stringent quality standards in the drive technology industry. They work well on both simple (1 or 2 axes) and complicated (up to 256 axes) applications.
In addition to the typical servo motor, we may also provide you specially made substitutes:
- Size: 80*50*50mm - 400*200*200mm, .etc
- Power Rating: 100W - 10KW
- Torque Range: 0.5 Nm to 100 Nm, .etc
- Cooling Method: Air-cooled or Water-cooled
- Phase: Single - phase, 2 phase, 3phase ac servo motors
Home / AC Servo Motor
By Types
Asynchronous
- Slip: Necessary for torque, causing slight rotor and field speed difference.
- Robustness: Generally more robust and capable of handling harsh environments.
- Control Complexity: Simpler control but less precise than synchronous motors.
Synchronous
- No Slip: The rotor synchronizes with the stator field for precise control.
- Precision: Excellent speed and position control for precision applications.
- Efficiency: Higher efficiency as there is no slip-related loss.
Comparison Table
| Parameter | AC Asynchronous Servo Motor | AC Synchronous Servo Motor |
| Efficiency | ~85-90% | ~90-95% |
| Typical Power Range | 0.1 kW to 100+ kW | 0.1 kW to 50+ kW |
| Typical Speed | 0-3000 RPM | 0-6000 RPM |
| Feedback Devices | Incremental encoders, resolvers | Absolute encoders, resolvers |
By Phase
3-Phase
- Design: 3-phase AC servo motors Uses three-phase power supply.
- Voltage Supply: Typically 230V or 400V
- Torque Range: 0.1 Nm to 1000 Nm+
- Efficiency: 85% to 95%
2-Phase
- Design: 2- phase AC servo motor uses two-phase power supply.
- Voltage Supply: Typically 110V or 230V
- Torque Range: 0.05 Nm to 50 Nm
- Efficiency: 75% to 85%
Single-Phase
- Design: Single-phase AC servo motor uses single-phase power supply.
- Voltage Supply: Typically 110V or 230V
- Torque Range: 0.01 Nm to 20 Nm
- Efficiency: 50% to 75%
From 0 to N - Full Motor Solutions
By Control Methods
Open-Loop Control
- Basic control method where the motor operates without feedback.
- Commands are sent based on predefined parameters or sequences.
Closed-Loop Control
- Compares encoder or resolver feedback with required position, speed, or torque.
- Controller adjusts the motor's operation to minimize error and maintain accuracy.
Speed Control
- Regulates the motor's spinning speed.
- Uses PID control to maintain speed despite load variations.
Position Control
- Controls the precise position of the motor shaft.
- Requires encoder feedback to maintain the desired position.
Torque Control
- Controls the torque or force that the motor applies.
- Essential for applications needing consistent force, like robotic arms or machining.
Featured products
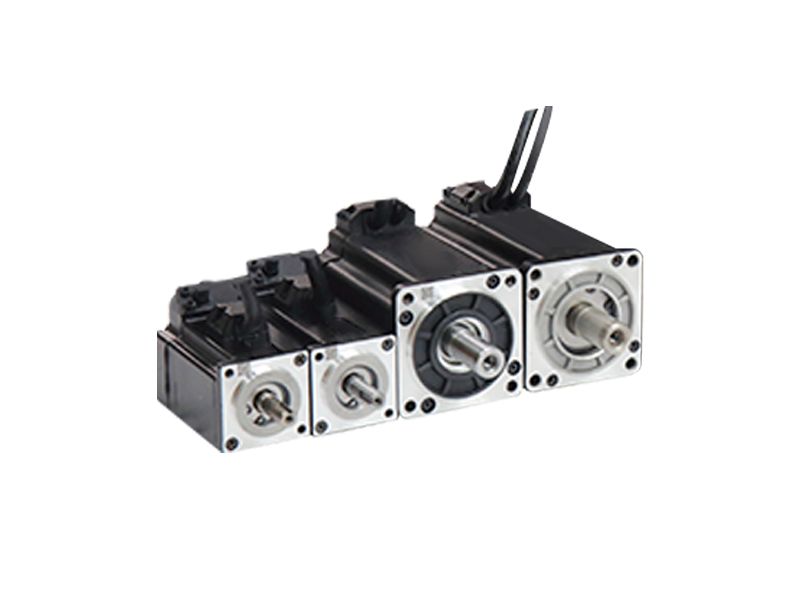

Series 1
- Pole Pairs: 3/4
- Voltage: 220VAC 380VAC
- Rated Power Range: 50w-3kw
- Complete flange range: 40mm, 60mm, 80mm, 110mm, 130mm, 150mm,180mm
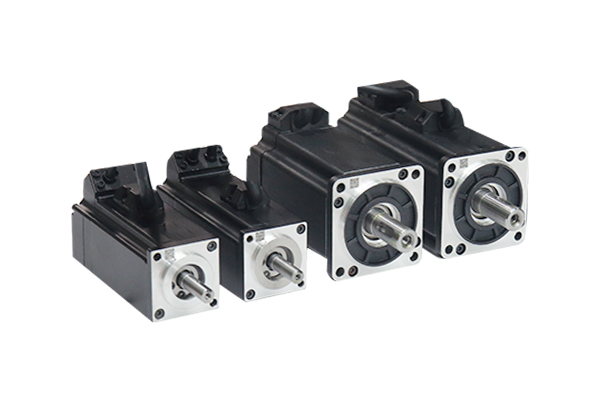

Series 2
- Pole Pairs: 5
- Voltage: 220VAC 380VAC
- Rated Power Range: 50w-1kw
- Flange Range: 40mm, 60mm, 80mm
Applications
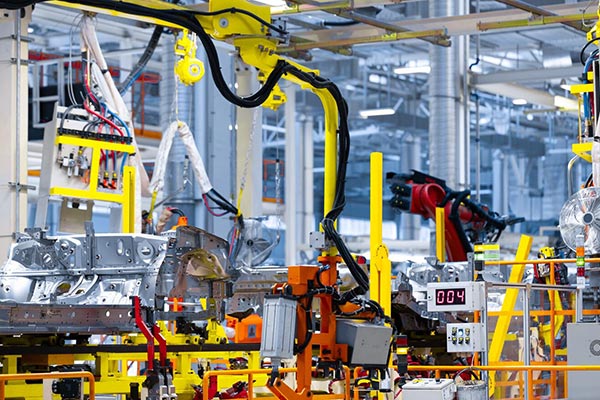

Industrial Automation
- CNC Machines: AC servo spindle motor offer precise control, essential for CNC machinery accuracy.
- Assembly Lines: Used for precise, repeatable tasks like pick-and-place operations.

Packaging Industry
- Labeling Machines: Ensure precise placement of labels on products.
- Filling machines: These machines precisely control filling solids or liquids into containers.

Medical Equipment
- MRI Machines: Provide precise control of the imaging components.
- Surgical Robots: Used for precise and controlled movements in minimally invasive surgeries.

Renewable Energy
- Wind Turbines: Designed to maximize energy absorption by adjusting the blade pitch.
- Solar Trackers: Ensure precise alignment of solar panels with the sun.
FAQ
What distinguishes a DC servo motor from an AC servo motor, in particular?
AC servo motors offer efficient, precise, high-speed performance. DC servo motors provide high starting torque, simpler control, but need more maintenance.
How does the price of an AC servo motor compare to that of a DC servo motor?
Generally speaking, AC servo motors are more expensive than DC servo motors because of their intricate design, sophisticated control systems, and increased accuracy.
What factors should be considered when choosing between an AC servo motor and a DC servo motor for an application?
Consider performance requirements (efficiency, precision), price, maintenance needs, power requirements, and application specifics such as load conditions and control complexity.
What are the typical applications for AC servo motors?
AC servo motors are used in industrial automation, robotics, CNC machines, renewable energy, and high-precision machinery.
Why might a 750W DC servo motor be preferred over an AC servo motor in certain applications?
A 750W DC servo motor is preferred for its low cost, simple control, high starting torque, and suitability for small-scale applications.
What are the maintenance requirements for DC vs. AC servo motors?
AC servo motors require less maintenance due to no brushes. DC servo motors need regular maintenance for brushes and commutators.