Servo motors are crucial parts of many applications, including automation, robotics, CNC machinery, and manufacturing. To guarantee optimum performance, cost effectiveness, and energy efficiency, selecting the appropriate servo motor size is essential.
This guide provides an in-depth look into servo motor sizes, their specifications, and how to select the right one for your application.
What Is a Servo Motor?
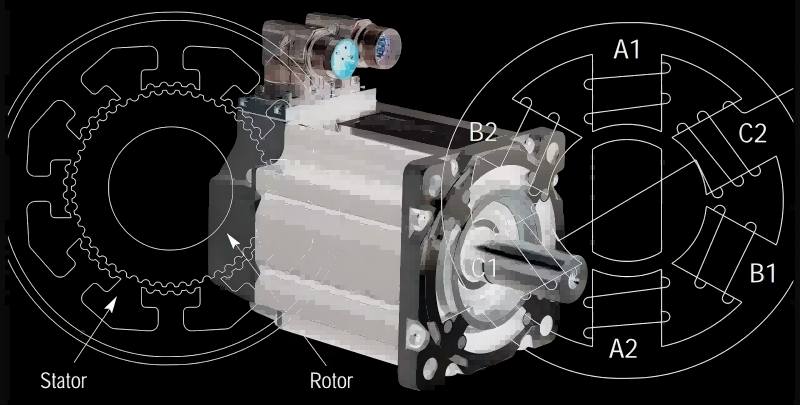
A servo motor is a type of linear or rotary actuator that enables accurate control of acceleration, speed, and angular position.A motor and a feedback sensor are coupled for closed-loop control. Industries needing precise positioning and speed control make extensive use of servo motors.
Key Features:
- High precision
- Quick response time
- Compact design
- Customizable torque and speed
Why are Servo Motor Sizes Important?
The size of a servo motor impacts its torque, speed, and ability to perform under load. Choosing an incorrectly sized motor can result in:
- Undersizing: Insufficient torque, overheating, and reduced lifespan.
- Oversizing: Unnecessary cost, larger space requirements, and inefficiency.
To ensure optimal performance, understanding motor size classifications and their specifications is vital.

Classification of Servo Motors by Size
Servo motors come in a variety of sizes, ranging from miniature motors for small electronic devices to large motors used in industrial machinery. The sizing of a servo motor depends on several factors, including:
- Torque Requirements: The amount of torque needed to move or hold a load.
- Speed Requirements: The speed at which the motor needs to operate.
- Load Inertia: The resistance of the load to changes in motion.
- Application Type: Whether the motor will be used for positioning, continuous motion, or both.
Key Factors in Servo Motor Sizing
Understanding your application and the capabilities of the motor is essential to proper servo motor sizing. The primary considerations are as follows:
Torque
Servo motors are rated by their torque output, which is usually expressed in Newton-meters (Nm) or ounce-inches (oz-in). The torque needed for your application determines the size of the motor.
- Continuous Torque: The torque a motor can deliver continuously without overheating.
- Peak Torque: The highest torque that a motor can produce during brief periods of time.
Speed
The motor’s speed is typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). Applications requiring high-speed movements may need smaller, lighter motors with higher RPM capabilities.
Power
The product of torque and angular velocity is used to compute power. For applications that need higher power, larger servo motors could be required.
Physical Dimensions
Servo motors are available in different physical sizes, often determined by the frame size. Common frame sizes are based on industry standards, such as NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) sizes.
Common Servo Motor Sizes
Here is a breakdown of common servo motor sizes and their typical applications:
| Servo Motor Size | Torque Range | Speed Range | Typical Applications |
| Micro | < 0.1 Nm | 1000–5000 RPM | Small robots, drones, hobbyist projects |
| Small | 0.1–1 Nm | 1000–6000 RPM | Medical gadgets, 3D printers, and CNC machines |
| Medium | 1–10 Nm | 500–3000 RPM | Industrial robots, packaging machines |
| Large | > 10 Nm | 100–1500 RPM | Heavy machinery, conveyor systems |
Torque vs. Speed: Understanding the Trade-off
Servo motors operate within a trade-off between torque and speed. The faster a motor runs, the less torque it can deliver. Conversely, motors delivering high torque often have lower maximum speeds. This relationship is typically represented on a torque-speed curve.
Sample Torque-Speed Curve
Below is a general representation of a torque-speed curve for a servo motor:
- Region 1: Continuous torque at lower speeds.
- Region 2: Peak torque for brief durations.
- Region 3: Reduced torque at high speeds.
| Speed (RPM) | Torque (Nm) |
| 500 | 10 |
| 1000 | 8 |
| 2000 | 6 |
| 3000 | 4 |
| 4000 | 2 |
Sizing Example: Selecting a Servo Motor for a CNC Machine
Imagine you’re designing a CNC machine that requires the following:
- Load inertia: 0.02 kg·m²
- Speed: 1500 RPM
- Continuous torque: 3 Nm
- Peak torque: 6 Nm
Using these parameters, you would:
- Select the Speed Range: Choose a motor capable of at least 1500 RPM.
- Check Torque Requirements: Look for a motor delivering 3 Nm continuous torque and 6 Nm peak torque.
- Match Inertia: Ensure the motor’s inertia matches or is slightly higher than the load inertia for stability.
For this example, a medium-sized servo motor would likely be appropriate.
NEMA Servo Motor Sizing Chart
To simplify the selection process, here is a general chart showing typical servo motor sizes and their specifications:
| Frame Size | Continuous Torque (Nm) | Peak Torque (Nm) | Speed (RPM) | Applications |
| NEMA 17 | 0.2–0.5 | 0.5–1.0 | 3000–5000 | Small robots, 3D printers |
| NEMA 23 | 0.5–2.0 | 2.0–4.0 | 1000–3000 | CNC machines, packaging |
| NEMA 34 | 2.0–8.0 | 8.0–16.0 | 500–1500 | Industrial automation, robots |
| Custom Large | > 8.0 | > 16.0 | 100–500 | Conveyor belts, heavy lifting |
Steps to Choose the Right Servo Motor Size
- Define Application Requirements: Determine torque, speed, and load inertia.
- Review Motor Specifications: Compare specifications of available motors with your requirements.
- Consider Physical Constraints: To make sure the motor will work with your machine, check its physical dimensions.
- Run Simulations: Use simulation tools or software to verify the motor’s performance under expected operating conditions.
- Evaluate Environmental Factors: Consider heat dissipation, vibration, and mounting requirements.
Benefits of Proper Servo Motor Sizing
- Efficiency: Avoids energy wastage and overheating.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces initial and operational costs.
- Reliability: Ensures long-term operation without failures.
- Performance: Delivers precise control and accuracy.
Future Trends in Servo Motor Design
As technology evolves, servo motors are becoming smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient. Key trends include:
- Miniaturization: Micro servo motors with higher torque for compact applications.
- Integration: Built-in controllers for plug-and-play functionality.
- Energy Efficiency: Improved designs reducing power consumption.
Conclusion
Choosing the right servo motor size is a critical step in designing an efficient and cost-effective system. Understanding the relationship between size, torque, and application requirements ensures optimal performance. By considering factors like load requirements, environmental conditions, and system compatibility, and consulting with a trusted servo motor manufacturer, you can select a servo motor that meets your specific needs.