Stepper motors play an important role in many robotics, automation, and precision control applications. They are perfect for positioning duties since they can provide accurate, repeatable movements. However, when choosing a stepper motor, size is a crucial consideration. A stepper motor’s torque, speed, and overall performance are all impacted by its size.
This comprehensive guide explores stepper motor sizes, their classifications, and how to select the appropriate size for different applications.

Stepper Motor Sizes
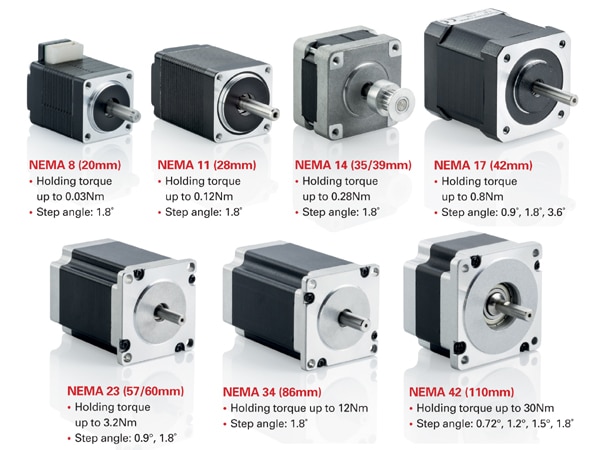
Stepper motors come in different sizes, which refer to the physical dimensions of the motor, primarily the frame size, and the body length. Usually, the frame size is stated in accordance with NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) guidelines. These standardized sizes help ensure that motors from different manufacturers fit within certain mounting specifications.
Common Frame Sizes of Stepper Motors
| NEMA Size | Frame Dimensions (inches) | Typical Torque Range (oz-in) | Applications |
| NEMA 8 | 0.79 x 0.79 | 1–5 | Miniature devices, small robotics |
| NEMA 11 | 1.1 x 1.1 | 5–15 | 3D printers, compact mechanisms |
| NEMA 14 | 1.4 x 1.4 | 10–20 | Medical instruments, light-duty automation |
| NEMA 17 | 1.7 x 1.7 | 20–60 | CNC machines, 3D printers, general-purpose automation |
| NEMA 23 | 2.3 x 2.3 | 100–200 | Industrial machines, robotics |
| NEMA 34 | 3.4 x 3.4 | 300–1000 | Heavy-duty CNC, industrial automation |
| NEMA 42 | 4.2 x 4.2 | 1000+ | Large-scale machinery, conveyor systems |
Understanding NEMA Ratings
The NEMA size defines the faceplate dimensions of the motor in inches. The faceplate of a NEMA 17 motor, for instance, is 1.7 inches on each side. While the frame size provides a general idea of the motor’s footprint, the body length, which varies within each frame size, determines the motor’s torque output and power.
How Does Stepper Motor Size Affect Performance?
The size of a stepper motor affects its torque, speed, and heat dissipation capabilities. Here’s how different sizes impact performance:
Torque
Larger stepper motors typically produce higher torque. This is because they have larger stators and rotors, allowing for greater magnetic force and a higher number of windings. The body length also influences torque, as a longer motor within the same frame size can house more windings and produce greater magnetic flux.
Speed
Motor size affects speed capabilities as well. Smaller stepper motors, such as NEMA 8 or NEMA 11, are well-suited for applications requiring quick, short movements. However, they may not maintain torque at higher speeds. Larger motors, like NEMA 23 or NEMA 34, can sustain higher torque at lower speeds, which is ideal for applications requiring controlled, high-power movements.
Heat Dissipation
Because of their greater surface area, bigger motors may frequently disperse heat more efficiently. This allows them to run at higher current levels without overheating, compared to smaller motors that may require additional cooling mechanisms when run at high power.
Common Stepper Motor Sizes and Their Applications
NEMA 8 and NEMA 11
These small motors are often used in devices where space is at a premium. NEMA 8 stepper motors are frequently found in miniature devices and precision instruments, while NEMA 11 motors are common in compact systems such as small 3D printers and lightweight robotic arms.
NEMA 14
NEMA 14 motors provide a good mix of adequate torque and small size. They are commonly used in light-duty automation tasks, small CNC machines, and medical devices.
Torque vs. Size Comparison Chart:
| NEMA Size | Frame Size (inches) | Torque (oz-in) | Application |
| 8 | 0.79 x 0.79 | 1–5 | Micro-robotics |
| 11 | 1.1 x 1.1 | 5–15 | 3D printers, compact robotics |
| 14 | 1.4 x 1.4 | 10–20 | Medical instruments |
NEMA 17
NEMA 17 motors are among the most widely used stepper motors, as they strike an excellent balance between size and power. They are commonly used in 3D printers, general-purpose robotics, and smaller CNC machines. With torque typically ranging from 20 to 60 oz-in, NEMA 17 motors offer sufficient power for a wide variety of precision tasks.
NEMA 23
For industrial and semi-professional applications, NEMA 23 motors provide the necessary torque and reliability. These motors are often found in industrial 3D printers, larger CNC machines, and automation systems. They have a torque range of 100 to 200 oz-in, making them suitable for tasks requiring more force and stability.
Performance Comparison Chart for NEMA 17 vs. NEMA 23:
| Aspect | NEMA 17 | NEMA 23 |
| Frame Dimensions | 1.7 x 1.7 inches | 2.3 x 2.3 inches |
| Torque | 20–60 oz-in | 100–200 oz-in |
| Typical Applications | 3D printers, light CNC | Industrial CNC, robotics |
NEMA 34 and NEMA 42
For heavy-duty industrial applications, larger motors such as NEMA 34 and NEMA 42 are required. These motors provide high torque, often exceeding 1000 oz-in. They are suitable for applications like large-scale CNC milling machines, conveyor systems, and other industrial automation tasks.
Gian Featured Products
Choosing the Right Stepper Motor Size
Application Requirements
The key to selecting the appropriate stepper motor size lies in understanding the specific requirements of the application. Here are some factors to consider:
- Load Torque: Calculate how much torque is required to transfer the load efficiently. This will help select the correct frame size and body length.
- Speed Requirements: Ensure the motor can provide sufficient torque at the operating speed needed for the application.
- Space Constraints: If the space is limited, choose a compact motor like NEMA 8 or NEMA 11.
- Thermal Management: Consider the motor’s ability to dissipate heat, especially for continuous or high-power applications.
Sample Application Scenarios
| Application | Recommended Motor Size | Reason |
| 3D Printer Extruder | NEMA 17 | Balance of torque and compact size |
| Desktop CNC Machine | NEMA 23 | Higher torque for precision cutting |
| Conveyor Belt System | NEMA 34 or NEMA 42 | High torque for heavy-duty industrial work |
| Medical Equipment | NEMA 14 | Compact size with sufficient torque |
Conclusion
Selecting the right stepper motor size is crucial for optimizing the performance, efficiency, and reliability of a motion control system. Understanding the trade-offs between different sizes helps engineers make informed decisions that align with the specific requirements of their applications. The right motor size ensures that the system can deliver the required torque and speed while maintaining energy efficiency and avoiding overheating. From the compact NEMA 8 used in micro-robotics to the robust NEMA 42 suitable for large-scale industrial machinery, stepper motor sizes offer solutions for a wide range of needs.
Moreover, partnering with a reputable stepper motor manufacturer can further streamline the selection process. A trusted manufacturer can provide guidance on selecting the best motor size for your application, ensuring that the motor not only meets the mechanical and electrical specifications but also aligns with the operational demands. Please contact Gian Transmission, we will provide a customized solution.