Micro Motor Manufacturer
We specialize in designing and manufacturing a range of low-voltage miniature motors, including brushed and brushless DC motors, stepper motors, and servo motors, with optional encoder integration. These motors are compact, lightweight, energy-efficient, and designed to minimize electromagnetic interference, making them easy to use in a variety of applications.
The parameters we can provide are as follows, we can provide more tailored specs if you have one in mind :
- Size: Length: 5mm-150mm, Diameter: 4mm-100mm
- Voltage: 1.5v-24v
- Weight: 5g-150g
- RPM: 300rpm-50000rpm
Home / Micro Motor
By Size
Miniature motors come in a variety of sizes, typically designed to be compact for use in small devices. If you have any customized requirements, you can contact us with drawings.
Diameter:4 mm to 12 mm
- The diameter of the motor housing, usually measured at the widest point of the cylindrical body.
- The motor's diameter often dictates its power capacity and torque output. Smaller diameters suit low-power uses; larger ones provide higher torque.
Length: 10 mm to 25 mm
- The length of the motor body from the base to the end, excluding the shaft.
- The length of a micro motor is closely related to its power and torque, as a longer motor can house more extensive windings and magnets.
Shaft Diameter: 0.8 mm to 2 mm
- The motor's output shaft diameter transmits rotational motion to attached components.
- Larger shaft diameters (up to 2 mm) are stronger, allowing for more robust attachments and handling higher loads.
Shaft Length: 5 mm to 10 mm
- The length of the output shaft that protrudes from the motor body.
- Shaft length determines how easily the motor can connect with external components. The longer shaft provides versatility in mounting and aligning with other components.
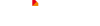
Here are some common sizes for our mini electric Motor
 |
4mm x 8mm (N10 size) | Common in mini vibrational devices or ultra-compact designs. |
| 6mm x 12mm (N20 size) | Often used in robotics and small electronics projects. | |
| 8mm x 16mm (N30 size) | Slightly larger, providing more torque for small robotics. | |
| 10mm x 20mm (N40 size) | Offers more power and is used in mini-robots and model projects. | |
| 15mm x 25mm | Used in slightly larger hobbyist applications that still require compact motors. | |
| 16mm x 30mm | Common in small tools or high-torque compact systems. |
By Current
We offer both AC and DC miniature motors, ideal for various applications requiring precision, efficiency, and compact design.

AC
- Run on alternating current (AC) power.
- AC micro motors are more commonly used in stationary or continuous-use applications with a stable power supply, offering smooth and efficient operation at constant speeds.
DC
- Run on direct current (DC) power.
- DC micro motors are preferred for portable, battery-operated devices where ease of speed control, lightweight design, and cost-effectiveness are crucial.
From 0 to N - Full Motor Solutions
By Commutation Method
Both motor types use electromagnetic induction for rotational motion, differing in brushes vs. electronic controllers.
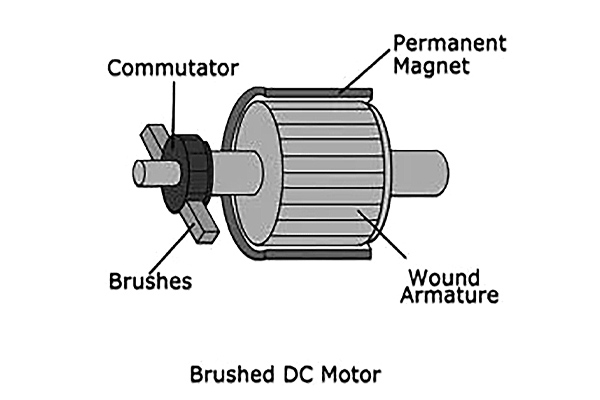
Brushed
- Brushed micro motors use brushes to transfer current to the rotor's windings, which leads to lower efficiency due to friction. Their lifespan is shorter, typically ranging from 1,000 to 10,000 hours, due to wear on the brushes.
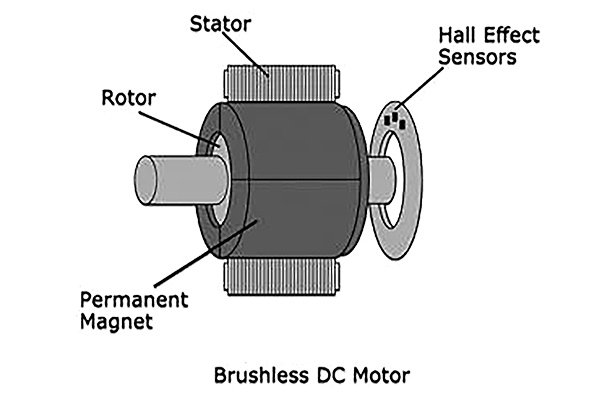
Brushless
- Micro brushless motors do not require physical brushes because they employ an electronic controller to manage the current flowing through the stator windings. This results in higher efficiency (80-90%) and a much longer lifespan, often exceeding 20,000 hours, due to the absence of brush wear.
By Type
Micro coreless, stepper, and servo motors convert electrical energy to mechanical motion, are compact, DC-powered, and generate torque electromagnetically.

Micro Coreless Motor
- The rotor uses a lightweight coil instead of a metal core. Uses brushes and commutator, with faster acceleration due to lighter rotor.
- Voltage: 1.5V - 24V
- Speed: 700 - 30,000 RPM
- Torque: 0.1 - 100 mN·m
Micro Stepper Motor
- They divide rotation into steps, with microstepping providing smoother motion and greater precision by energizing coils in sequence for fractional movement.
- Voltage: 2V - 12V
- Speed: 100 - 10,000 RPM
- Accuracy: 1.8° per step

Micro Servo Motor
- They use feedback mechanisms and PWM signals to precisely control angular position, adjusting through a feedback loop for accuracy.
- Voltage: 4.8V - 24V
- Speed: 0.1 to 0.2 seconds per 60° rotation
- Rotation: Typically 180°, but continuous rotation models exist.
3 Types of Micro Motor Comparison
Feature | Micro Coreless Motor | Micro Stepper Motor | Micro Servo Motor |
Design | Brushed DC with lightweight rotor | Multiple coils and discrete stepping | Brushed DC with feedback loop |
Operation | Constant speed, controlled by voltage | Step-by-step rotation controlled by pulses | Positioning control via PWM signal |
Precision | Moderate | High precision | Moderate precision, typically 1.5°/step |
Speed | High speed (up to 30,000 RPM) | Slower speed (typically 1,000 – 10,000 RPM) | Moderate (typically 0.1 – 0.2 s/60°) |
Torque | Moderate | High torque at low speeds | Low to moderate (up to 2 N·m) |
Applications

Consumer Electronics
- Micro vibration motor: Used in mobile phones, game controllers, and other portable devices for haptic feedback (vibration alerts).
- Small Fans: In cooling systems for computers, laptops, and handheld electronics.
- Camera Stabilization: For controlling gimbals and lens focusing in digital cameras and smartphones.

Robotics
- Actuators: In small robots, robotic arms, drones, and toys, where precise control of movement is required.
- Servo Motors: To control the position of robot joints, wheels, or other moving parts in a robotic system.
- Micro Robots: In miniature robots for medical, military, or research purposes, where space and weight are critical.

Medical Devices
- Miniature Pumps: For drug delivery systems, insulin pumps, or small-scale fluid transfer devices.
- Dental Equipment: Micro motors are used in dental drills, cleaning, and other precision tools.
- Surgical Instruments: In robotic surgery or precision tools used for micro-surgeries.

Automotive
- Electric Actuators: For controlling small functions in vehicles like seat adjustments, mirrors, or window lifts.
- Small Pumps: For fuel systems or cooling systems.
- Sensors and Control Systems: Micro motors in sensors or devices that require small but efficient motion for accurate measurements.

Industrial and Automation
- Micro Pumps: In industrial fluid management or chemical processes.
- Precision Drives: For small-scale automated machines, such as 3D printers, CNC machines, or conveyor systems.
- Vibration Systems: For testing equipment or simulating real-world conditions.

Aerospace
- Drones: For small-scale unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), micro motors provide propulsion and control.
- Satellite Equipment: Used in actuators for antennas or control surfaces in compact satellite systems.
- Microthrusters: In aerospace applications for fine control in spacecraft navigation.