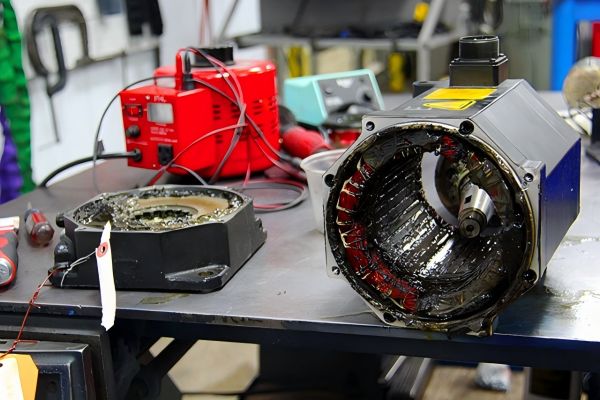
Servo motors are critical components in modern machinery, ranging from industrial robots and CNC machines to conveyor belts and robotics. These motors can effectively manage a range of loads and offer precise motion control. However, like all mechanical and electrical components, they are subject to wear and tear and may require maintenance or repair over time. In this article, we will explore the key precautions to take when repairing a servo motor, including key components to check during repair, when to repair a servo motor, the tools used, common mistakes to avoid, and how to calibrate a servo motor after a repair. We will also go over crucial safety factors to guarantee a successful and secure repair procedure.
Key Components to Check During Repair
When repairing a servo motor, it is essential to inspect various components to ensure proper functioning. Here are the critical parts that should be checked:
Motor Shaft and Bearings
The motor shaft and bearings are subject to mechanical stress and friction, which can lead to wear over time. Look for any indications of bends, excessive wear, or misalignment in the shaft. The bearings should be tested for smooth rotation and any unusual noises that indicate a fault.
Encoder
The encoder provides feedback about the motor’s position and speed, which is vital for precise movement control. If the motor’s performance is erratic or inconsistent, the encoder could be malfunctioning. Verify that the wiring of the encoder is clean, undamaged, and clear of dust or dirt. Any damage to the encoder can affect the motor’s performance, so a careful check is necessary.
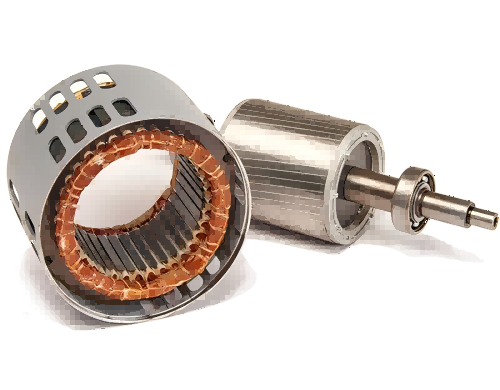
Stator and Rotor
The stator and rotor are the heart of the motor and play a crucial role in generating torque. Look for any indications of cuts, burns, or excessive wear on the stator windings. Similarly, check the rotor for any unusual wear patterns, which may indicate that the motor is operating outside of its design parameters. If you see any anomalies, think about swapping out the broken components.
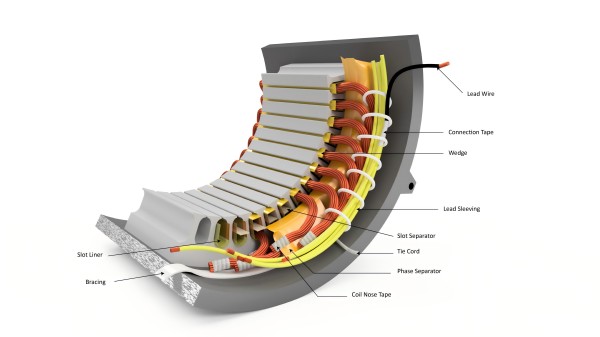
Motor Insulation
Motor insulation is crucial for preventing electrical shorts and ensuring that the motor operates safely. Inspect the insulation of the windings, particularly for signs of cracking, fraying, or contamination by oil or other substances. Damaged insulation should be replaced to prevent short circuits, which can lead to further damage to the motor.
Power Supply and Control Circuitry
Issues with power supply or control circuitry can often manifest as irregular motor behavior. Check the connections and components in the power supply circuit, such as capacitors, resistors, and diodes. Inspect the controller for any faulty connections or damaged circuits that could be affecting motor performance.
When to Repair the Servo Motor
Knowing when to repair a servo motor is crucial to avoid unnecessary downtime and cost. Here are some signs that your servo motor needs repair:
Unusual Noise or Vibration
If the motor starts producing strange noises, such as grinding, buzzing, or high-pitched sounds, this may indicate mechanical wear or electrical issues. Unusual vibration can also signal misalignment, bearing failure, or damage to other internal components.
Performance Errors or Precision Losses
If the motor starts behaving erratically, such as overshooting, stalling, or not reaching the desired position, there could be a problem with the encoder, feedback system, or electrical components. If precision is compromised, immediate repair is necessary.
Overheating
If a servo motor overheats during operation, it can indicate problems with the motor windings, bearings, or insufficient cooling. The motor may sustain irreversible damage from overheating, including deterioration of the insulation and other parts. Always address overheating issues immediately to prevent long-term damage.
Motor Stops Working or Doesn’t Start
If the motor refuses to start or stops working unexpectedly, it may be a sign of an electrical failure, control issues, or damage to key components such as the power supply, encoder, or stator.
Visible Physical Damage
If there is visible physical damage to the motor, such as cracks in the casing, burnt components, or external deformation, it is an obvious sign that the motor needs attention. To find any damage before it becomes worse, a visual inspection should be done on a regular basis.
Tools Used to Repair Servo Motors
Proper tools are essential for effective servo motor repair. The following list of instruments is frequently used to fix servo motors:
Multimeter
A multimeter is essential for checking the electrical components of the servo motor. It can be used to test the voltage, current, resistance, and continuity of circuits, as well as check for shorts or open circuits in the windings or control circuitry.
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is used to monitor the motor’s electrical signals, which helps diagnose issues with the encoder, feedback systems, and other electrical components. It is useful for identifying abnormal voltage spikes or irregularities in signal patterns.
Bearing Pullers
To remove bearings off the motor shaft without causing harm to the motor or nearby components, bearing pullers are necessary. When bearing replacement is necessary as part of the repair procedure, these instruments are utilized.
Insulation Resistance Tester
The resistance of motor windings and insulation is measured with an insulation resistance tester, sometimes referred to as a Megger. This tool helps detect insulation breakdown or leakage, which can lead to short circuits or motor failure.
Torque Wrenches
Torque wrenches are used to tighten components to the manufacturer’s recommended specifications. Proper torque is essential for preventing damage to the motor during assembly.
Cleaners and Lubricants
A variety of cleaners and lubricants are required to maintain and clean motor components. Cleaners remove dust, dirt, and oil from the motor parts, while lubricants ensure smooth movement of mechanical components such as bearings and the motor shaft.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Servo Motor Repair
When repairing a servo motor, it is crucial to avoid common mistakes that can lead to further damage or suboptimal performance. Here are some mistakes to avoid:
Using Incorrect Parts
Replacing faulty components with incorrect or low-quality parts can lead to further motor issues. Always ensure that the replacement parts match the specifications of the motor. Using cheap substitutes can compromise performance, efficiency, and reliability.
Inadequate Cleaning
A dirty motor can lead to overheating, increased wear, and poor performance. Always clean the motor thoroughly before reassembly, and remove any dust, dirt, or debris from internal components.
Ignoring Manufacturer Guidelines
A set of manufacturer instructions and specs are included with every servo motor. Ignoring these can result in improper assembly, calibration, or performance. Always refer to the motor’s manual or technical documentation during the repair process.
Failing to Test the Motor Before Reassembly
It’s essential to test the motor before reassembling it completely. Testing assists in confirming that all parts are operating as intended and that the repair was effective. Failing to test may result in rework and wasted time.
Overlooking Calibration
After repairs, servo motors frequently need to be calibrated to guarantee precise operation. Skipping the calibration process can lead to inaccurate movement, control issues, and mechanical strain.

How to Calibrate a Servo Motor After Repair
A servo motor must be calibrated after repair to function at its best. The procedures for calibrating a servo motor are as follows:
Set the Motor to Zero Position
Start by setting the motor to its zero position. Usually, to accomplish this, the motor is aligned with the home position or reference point. This ensures that the motor starts from a known position.
Adjust the Controller Settings
It is necessary to modify the controller settings to the specifications of the repaired motor. This includes setting the proper voltage, current limits, and control parameters. Use the motor’s manual to find the optimal settings for your application.
Test the Motor’s Response
To make sure the motor reacts appropriately to the control signals, put it through some tests. Test for smooth motion, correct speed, and accurate positioning. If any discrepancies are observed, adjust the controller settings or check the motor’s components again.
Fine-Tune the Feedback System
Servo motors rely on feedback systems, such as encoders, to maintain precise positioning. After repair, calibrate the feedback system to ensure that it is providing accurate data to the controller. Any misalignment in the feedback system can cause performance issues.
Perform Load Testing
Once the motor has been calibrated, perform load testing to check its ability to handle real-world conditions. This will verify that the motor can operate dependably in typical operational circumstances.

Servo Motor Repair Safety
Safety should always be a top priority when repairing servo motors. The following safety guidelines should be adhered to while performing repairs:
Power Off the Motor
Make sure the motor is unplugged from the power source before starting any repairs. Working on live electrical components can result in electric shock or further damage to the motor.
Put on the appropriate PPE (personal protective equipment).
Put on the proper PPE, such as safety goggles, gloves, and wrist straps that prevent static electricity. This will protect you from electrical shock, flying debris, and other hazards.
Handle Components with Care
Bearings and encoders are two delicate motor parts that are readily harmed by careless handling. Be gentle when working with these components and avoid using excessive force.
Ensure Proper Ventilation
Working with electrical components and lubricants can create fumes or heat. Ensure that the workspace is well-ventilated to prevent any hazards related to inhaling fumes or exposure to high temperatures.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
Always follow the servo motor manufacturer’s safety guidelines and instructions when repairing servo motors. The purpose of these instructions is to safeguard the motor and the technician while it is being repaired.
Conclusion
Repairing a servo motor requires careful attention to detail, knowledge of the motor’s components, and the use of the correct tools. By checking key components, recognizing when to repair, avoiding common mistakes, and following proper calibration procedures, you can ensure that the motor operates efficiently and safely. Always prioritize safety, follow best practices, and consult the manufacturer’s guidelines to minimize risks and maximize the lifespan and performance of the motor.