Coreless DC motors, in contrast to conventional DC motors, do away with the iron core in the rotor, producing a motor that is lightweight and sensitive. While coreless motors offer a variety of advantages, their unique design presents specific challenges when it comes to repair and maintenance.
Comprehending Coreless DC Motor Structure
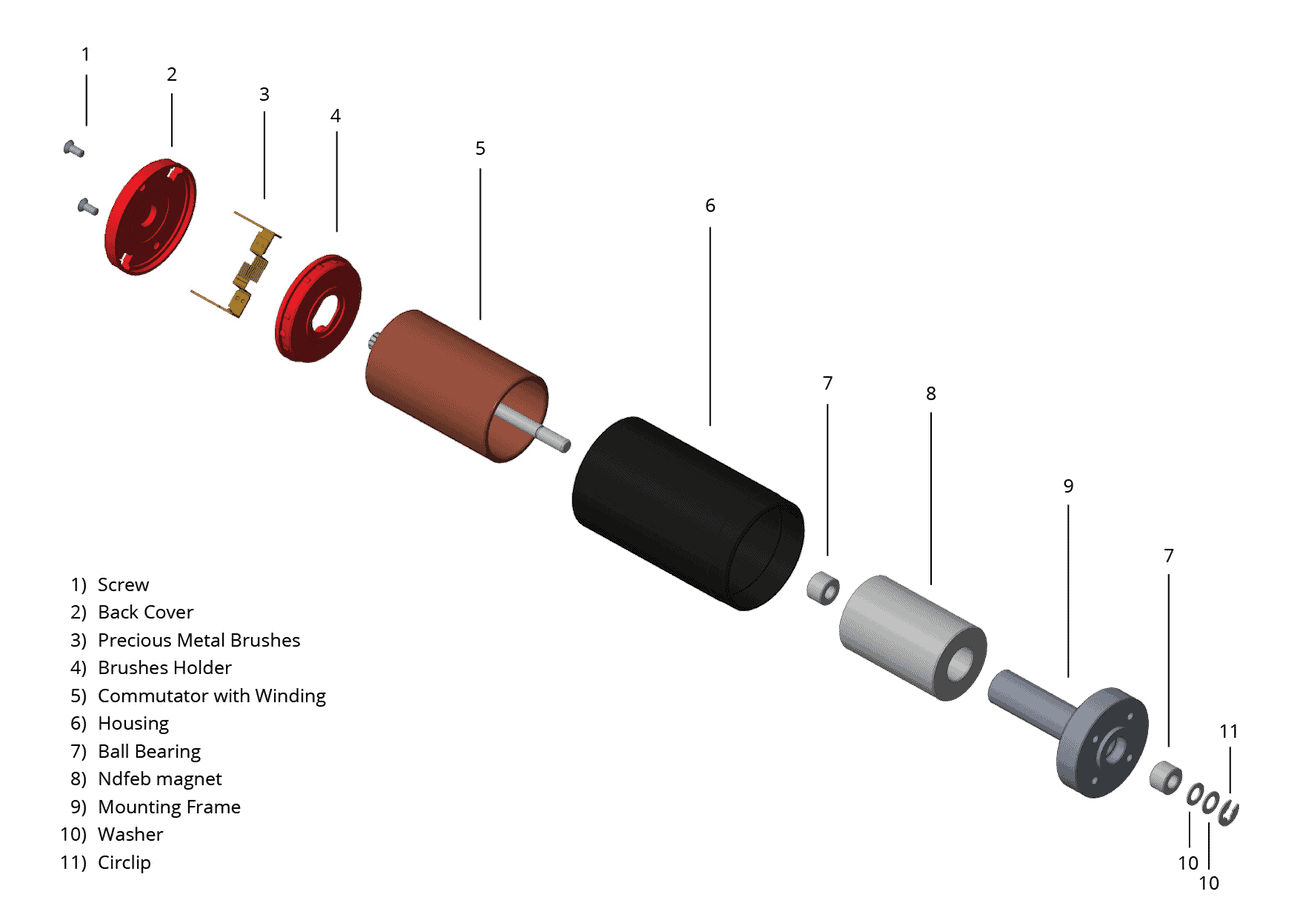
It’s important to comprehend the special construction of a coreless DC motor before beginning maintenance or repairs. Unlike conventional motors that use an iron core rotor, coreless DC motors feature a rotor made of a lightweight coil wound in a cylindrical shape. This design reduces the motor’s inertia, allowing for faster acceleration and improved dynamic response.
Key components of a coreless DC motor include:
- Rotor: The coreless rotor consists of lightweight copper windings, eliminating the need for an iron core.
- Stator: The permanent magnets that provide the magnetic field required for motor operation are housed in the stator.
- Brushes and Commutator: These are responsible for transferring current to the rotor windings and commutating the motor’s rotation.
- Bearings: Bearings support the rotor’s rotation and minimize friction between moving parts.
Common Issues with Coreless DC Motors
Despite their advantages, coreless DC motors can experience various problems due to wear and tear, improper use, or environmental factors. Understanding common issues will help diagnose problems and conduct timely repairs.
Brush and Commutator Wear
Brushes and commutators in coreless DC motors undergo mechanical contact during operation. The brushes deteriorate over time, resulting in poor electrical contact and higher resistance. This results in reduced performance, sparking, and overheating. Commutators can also wear unevenly or develop grooves, further affecting motor efficiency.
Bearing Wear and Failure
Bearings in coreless DC motors support the rotor’s smooth rotation. Bearings may become worn down over time as a result of pollution, friction, or inadequate lubrication. Worn bearings cause noise, vibration, and increased friction, which can damage the rotor and stator components.
Thermal Damage
Coreless DC motors operate at high speeds and generate heat during operation. Inadequate ventilation or excessive loads can cause the motor to overheat, leading to thermal damage to the windings, brushes, and insulation. Overheating reduces motor efficiency and can cause permanent damage to the rotor windings.
Contamination
Coreless DC motors are sensitive to dust, dirt, and moisture. Poor electrical contact and increased wear can result from contamination interfering with the commutator and brushes. Dust and debris can also damage the bearings, leading to premature failure.
Electrical Faults
Electrical issues such as short circuits, open circuits, or insulation breakdowns in the windings can occur due to prolonged use or excessive stress. These flaws cause partial motor failure, loss of power, or erratic motor performance.
Preventive Maintenance Practices for Coreless DC Motors
To increase the lifespan and reduce the cost of repairs for coreless DC motors, regular preventive maintenance is crucial. Your motor will continue to run as efficiently as possible if you follow the crucial maintenance steps mentioned below.
Inspection of the Commutator and Brush
Check the commutator and brushes often for indications of wear or damage. Worn brushes should be replaced promptly to ensure proper electrical contact. To get rid of any debris or carbon deposits, use a commutator stone or soft brush to clean the commutator. Use of excessively abrasive materials should be avoided as this might damage the commutator.
Lubrication of Bearings
To lessen friction and stop wear, coreless DC motor bearings should be greased on a regular basis. Use a high-quality lubricant designed for motor bearings, and avoid over-lubrication, which can attract dust and dirt. In the event that the bearings are sealed and pre-lubricated, replace them at the manufacturer’s suggested intervals.
Temperature Monitoring
Monitor the motor’s operating temperature to prevent overheating. Excessive heat can damage the windings and insulation, leading to motor failure. Make sure the motor is well-ventilated, and try not to operate it at high loads for extended periods of time. Consider using thermal protection devices or sensors to monitor temperature levels.
Prevention of Contamination
To avoid contamination, keep the motor and its surroundings clean. Install protective coverings or dust filters if the motor is being utilized in an unclean or dusty environment. Ensure that the motor is properly sealed to prevent the ingress of moisture or liquids, which can cause short circuits or corrosion.
Electrical Checks
Regularly check the motor’s electrical connections, wiring, and insulation for signs of wear or damage. Use a multimeter to measure resistance, voltage, and current levels to ensure that the motor is operating within its specified range. If you notice any irregularities, investigate further to identify potential electrical faults.
Troubleshooting Coreless DC Motor Problems
Troubleshooting is necessary to identify and fix performance issues with a coreless DC motor. The following list of typical symptoms along with potential causes:
| Symptom | Possible Causes |
| Motor fails to start | Worn brushes, open circuits, faulty wiring |
| Motor runs unevenly | Worn commutator, brush bounce, electrical faults |
| Excessive noise or vibration | Worn bearings, rotor imbalance, loose components |
| Overheating | Overloading, poor ventilation, damaged windings |
| Loss of power | Worn brushes, electrical faults, winding insulation damage |
Repairing Coreless DC Motors
In some cases, coreless DC motors can be repaired to restore performance and extend their lifespan. However, repairs should be conducted by skilled technicians with knowledge of motor mechanics and electronics.
Replacing Brushes and Commutators
Worn brushes are one of the most common issues in coreless DC motors. Replacing the brushes is a relatively simple repair that can significantly improve motor performance. To replace the brushes:
- Disconnect the motor from the power supply.
- Open the motor housing to access the brushes and commutator.
- Remove the worn brushes and inspect the commutator for damage.
- Clean the commutator and install new brushes.
- Reassemble the motor and test its performance.
It could be necessary to repair or resurface the commutator if it has deep grooves or is damaged.
Bearing Replacement
Worn or damaged bearings should be replaced to restore smooth motor operation. To replace the bearings:
- Remove the motor’s housing to access the rotor.
- Carefully extract the rotor and bearings.
- Clean the bearing seats and install new bearings.
- Reassemble the motor and ensure that the rotor spins freely without excessive friction or noise.
Ensure that you use high-quality bearings and proper lubrication during the replacement process.
Rewinding the Rotor
In cases of severe winding damage, such as short circuits or insulation breakdown, the rotor may need to be rewound. Rewinding involves replacing the damaged copper windings with new ones. This is a complex process that requires specialized equipment and expertise, so it is typically performed by professional motor repair shops.
Repairing Electrical Faults
If the motor experiences electrical faults, such as short circuits or open circuits, you will need to check the wiring, insulation, and windings. Use a multimeter to measure resistance and identify any faults in the electrical system. The windings of the motor can require repair or rewiring, depending on the extent of the damage.
Advanced Repair Procedures
In some cases, coreless DC motors may require more extensive repairs. Here are some advanced repair procedures that may be necessary:
Commutator Resurfacing
Over time, the commutator can develop grooves or uneven surfaces due to the constant contact with the brushes. This can cause poor electrical contact, leading to sparking and inconsistent motor performance.
- Solution: The commutator may need to be resurfaced using a commutator lathe or similar equipment. Resurfacing removes the grooves and ensures a smooth contact surface for the brushes.
Rewinding the Rotor
If the rotor windings become damaged due to overheating or excessive current, the motor may lose power or fail to operate entirely. In such cases, the rotor will need to be rewound.
- Solution: Rotor rewinding should be done by professionals with experience in coreless motor repair, as it requires precision and attention to detail to maintain the motor’s balance and performance.
Motor Alignment
Sometimes, misalignment of the rotor and stator can lead to poor motor performance or increased wear on the bearings and brushes.
- Solution: Check the alignment of the motor components and adjust as needed. Misalignment can be caused by improper mounting or mechanical stress during operation. Make sure the motor is attached firmly and that every part is positioned as it should be.
Best Practices for Extending Motor Lifespan
It is crucial to adhere to the following recommended practices in order to extend the lifespan of coreless DC motors:
- Avoid Overloading: Always operate the motor within its rated power and torque limits. Overloading the engine can lead to overheating and early component wear.
- Ascertain Appropriate Ventilation: Verify that the motor is not running in a hot or cramped space and that it has enough cooling.
- Monitor Operating Conditions: During operation, pay attention to the motor’s temperature, noise level, and vibration intensity.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the brushes, commutator, bearings, and electrical connections to catch issues early.
- Professional Servicing: For advanced repairs such as rotor rewinding or commutator resurfacing, always rely on professional services to avoid damaging the motor further.
Repair and maintenance of coreless DC motors requires attention to detail and routine inspections to ensure long-term reliability and performance. For more complex repairs, professional assistance may be required. Replacing the motor, however, can be the most economical course of action in situations involving significant damage or advanced age.
Gian Transmission is committed to providing after-sales service for the motors we sell. Our customers can always ask us questions about the motors if they have any questions.