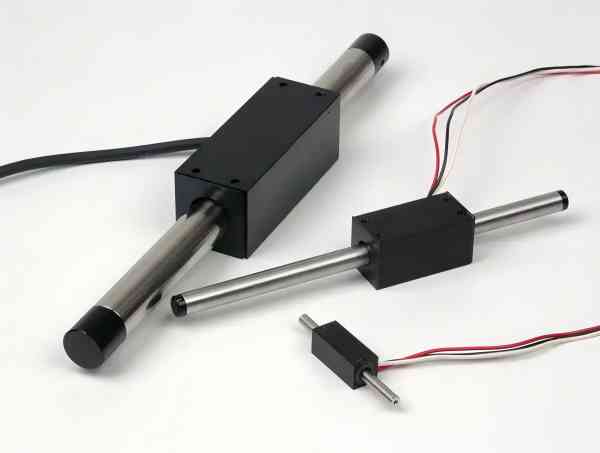
Servo motors come in many forms, with rotary and linear micro servos being two of the most common types. While both serve similar functions in terms of motion control, they differ significantly in design, performance, and applications. Understanding the differences between rotary servo motors and linear micro servos can help engineers, designers, and hobbyists make informed decisions when choosing the right motor for their projects.
This article explores the characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and specific use cases of rotary servo motors and linear micro servos, offering a detailed comparison that will guide your selection process. Along with this, we’ll highlight the cost differences, performance factors, and some practical examples to help you make an informed decision.
Introduction to Servo Motors
The primary difference between servo motors and standard motors is the addition of a feedback device, such as an encoder or resolver, which helps achieve closed-loop control. This feedback ensures the motor performs exactly as required, offering high precision in motion control tasks.
Servo motors fall into two primary groups based on the motion of their output:
- Rotary Servo Motors: These motors rotate around an axis, typically providing rotational movement.
- Linear Micro Servo Motors: These motors are designed to produce linear (straight-line) motion instead of rotational movement.
Rotary Servo Motors
An electric motor that revolves on a single axis is called a rotary servo motor. Applications requiring rotating movement frequently employ it. AC and DC servo motors are the most widely used varieties of rotary servo motors.
Key Components of a Rotary Servo Motor
- Motor (AC/DC): The main component that generates rotational motion.
- Feedback Device (Encoder or Resolver): Provides feedback to the controller to adjust the motor’s position.
- Controller/Driver: The electronic unit that controls the motor’s speed, position, and direction.
Advantages of Rotary Servo Motors
- High Precision and Control: Rotary servo motors offer high torque and speed precision, making them ideal for applications where precise rotational movement is critical.
- Wide Range of Applications: These motors are used in robotics, CNC machines, industrial automation, conveyor systems, and aerospace applications.
- High Efficiency: Rotary servo motors generally offer high efficiency, especially in applications requiring continuous rotation.
- Variety of Sizes and Capacities: Rotary servo motors are available in a wide range of sizes, making them suitable for both small and large-scale applications.
Disadvantages of Rotary Servo Motors
- Limited to Rotational Motion: While great for tasks requiring rotational movement, rotary servo motors cannot provide linear movement without additional components like lead screws or gearboxes.
- Higher Cost: High-precision rotary servos, especially those with encoders or specialized control systems, can be expensive compared to standard motors.
Common Applications for Rotary Servo Motors:
- Robotics: For precise movement control of robotic arms.
- CNC Machines: For accurate positioning in manufacturing processes.
- Automated Doors and Windows: For rotational motion in various automation systems.
- Drones and Aircraft: For controlling flight surfaces.
Linear Servo Motors
One kind of servo that generates linear motion, as opposed to rotating motion, is a linear micro servo motor. These motors are typically smaller and provide precise, controlled linear displacement. In applications requiring small, accurate linear movement, linear micro servos are frequently utilized.
Key Components of a Linear Servo Motor
- Motor and Gearbox: The motor drives the linear actuator via a gearbox or lead screw.
- Feedback Device: Like rotary servo motors, linear micro servos often feature feedback devices like potentiometers or encoders.
- Controller/Driver: Similar to rotary servo motors, the controller regulates the linear motion based on the feedback.
Advantages of Linear Servo Motors
- Linear Motion: Ideal for applications requiring straight-line motion, such as in small actuators, linear slides, or valve control.
- Compact Size: Linear micro servos are typically smaller than their rotary counterparts, making them suitable for confined spaces or smaller devices.
- Precision Control: Offers excellent precision in small movements, which is especially useful in delicate tasks, such as adjusting focus in cameras or controlling small robotic arms.
- Ease of Integration: Linear micro servos are relatively easy to integrate into designs that need straight-line motion without additional mechanical parts like lead screws or rails.
Disadvantages of Linear Servo Motors
- Limited Force and Stroke Length: Compared to rotary motors, linear servos typically have a limited stroke length and may not provide as much force over long distances.
- Lower Efficiency: Linear micro servos may be less efficient than rotary motors in certain applications, especially where high power or long stroke lengths are required.
Common Applications for Linear Servo Motors
- Small Robotics: Used in small robotic actuators for linear movement.
- Camera Systems: For controlling lens focus or zoom in cameras.
- Prototyping: Used in prototypes or models requiring precise linear displacement.
- Medical Devices: Employed in medical equipment that requires small, precise linear movements, such as in drug delivery systems.
Key Differences Between Rotary Servo Motors and Linear Servo Motors
| Feature | Rotary Servo Motor | Linear Servo Motor |
| Motion Type | Rotational motion around an axis. | Linear (straight-line) motion. |
| Applications | Robotics, CNC, conveyor systems. | Small robotics, camera systems, actuators. |
| Size | Varies from small to large sizes. | Typically smaller and compact. |
| Force | High torque and power. | Limited stroke length and force. |
| Cost | Higher for high-precision models. | Generally more affordable. |
| Efficiency | Generally high, depending on application. | May be less efficient than rotary motors in certain applications. |
| Precision | High precision, ideal for rotational tasks. | High precision for small linear tasks. |
| Additional Components | Gearbox or lead screw needed for linear motion. | Often integrated with gearboxes or lead screws. |
Cost Comparison: Rotary Servo Motor vs. Linear Servo Motor
The initial purchase price, maintenance costs, and application-specific needs must all be taken into account when calculating the cost of these motors. Generally, rotary servo motors are more expensive, particularly for high-torque, high-precision models. They are commonly used in industrial applications, which justifies their higher price. However, linear micro servos are typically less expensive, particularly for small-scale uses like precise positioning chores or hobby projects.
| Motor Type | Price Range (Low-End) | Price Range (High-End) |
| Rotary Servo Motor | $50 – $300 | $500 – $5000+ |
| Linear Micro Servo Motor | $10 – $50 | $100 – $500 |
Note: Prices vary depending on the torque, size, brand, and additional features of the motor.
Performance Considerations
Rotary Servo Motors
- Torque: Rotary servos are designed to deliver high torque, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They can handle large loads and high-speed operations effectively.
- Speed: These motors are generally fast, with some high-end models capable of spinning at speeds of up to 6000 RPM or higher.
- Precision: With advanced feedback systems, rotary servo motors can achieve highly precise rotational movement, crucial for tasks like CNC machining and robotic arms.
Linear Servo Motors
- Force: Linear servos are designed for smaller loads and typically offer lower force than their rotary counterparts. They work well in mild to medium-duty jobs.
- Stroke Length: Linear micro servos are limited in terms of stroke length, usually providing a few centimeters to a few inches of linear movement.
- Precision: They offer exceptional precision for small linear motions, making them ideal for delicate applications, such as focusing mechanisms or small actuators.
Applications for Rotary Servo Motors and Linear Servo Motor
Rotary Servo Motor Applications:
- Robotics: High-precision rotation is essential in robotic arms, drone actuators, and autonomous vehicles.
- CNC Machines: These are used for precise motion of cutting instruments or machined components.
- Automated Systems: Used in conveyors, automated sorting systems, and robotic pick-and-place mechanisms.
- Aerospace and Defense: Essential in controlling flight surfaces and actuating robotic arms in spacecraft.
Linear Servo Motor Applications:
- Model Robotics: For miniature robotic arms or grippers that require linear displacement.
- Camera Systems: These are used to adjust zoom or focus in cameras or projectors.
- Medical Equipment: Employed in devices requiring precise linear motion for dispensing or moving parts.
- Prototyping: Commonly used in small-scale prototypes and mock-ups that require precise but compact motion.
In summary, the choice between a rotary servo motor and a linear micro servo motor depends heavily on your application requirements. As a reliable servo motor manufacturer, Gian Transmission can help you select the right motor, whether you need rotational motion with high torque or linear motion with precision for industrial automation, robotics, or consumer applications.