CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines have completely changed how industries manufacture parts, components, and products in the precision machining space. Because CNC machines can create complicated, repeatable, and high-precision parts in large quantities, they are frequently employed in industries such as electronics, metalworking, aerospace, and automotive. At the heart of these machines are the servo motors, which are critical for their performance.
Servo motors are integral to the operation of CNC machines, driving the movements of the machine’s axes and controlling the positioning and speed of various components with high accuracy. In this article, we will explore the role of servo motors in CNC machines, their types, advantages, and applications, and how they contribute to the efficiency and accuracy of these high-tech systems.
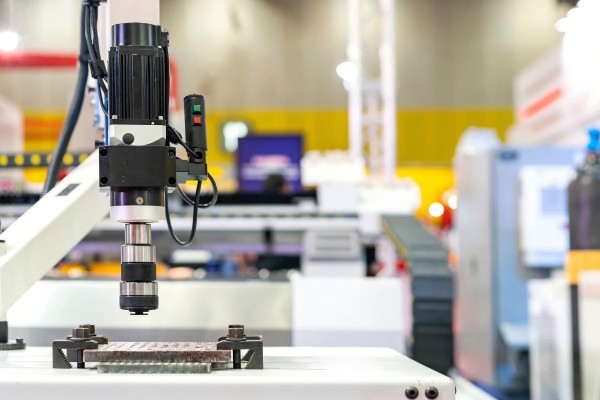

Understanding CNC Machines
Before diving into the specifics of servo motors, it’s essential to understand the basics of CNC machines and their operational requirements.
A CNC machine works by translating a computer-aided design (CAD) file into a set of instructions that regulate the tool’s (or workpiece’s) motion. These instructions, depending on the machine, direct the movements along three or more axes. There are several kinds of CNC machines:
- Milling Machines: Used to cut, shape, or drill materials.
- Lathes: Primarily used for turning operations.
- Laser Cutters: Utilize focused laser beams for cutting materials.
- 3D Printers: Parts are made by building up layers of material.
The motor system in a CNC machine is responsible for ensuring these tools or workpieces move along their respective paths with extreme accuracy. The role of servo motors is vital in controlling the precision of these movements.
What Is a Servo Motor?
An electric motor type called a servo motor is made to control acceleration, velocity, and angular position precisely. The ability of servo motors to precisely rotate to predetermined locations is one of their distinguishing features. In contrast to regular motors, which operate continuously at a set speed, servo motors are managed by feedback systems that continuously assess and modify their performance.
Key Features of Servo Motors:
Precision: Servo motors can achieve highly accurate positioning, which is essential for CNC machines that require exact control over the movement of tools or workpieces.
Feedback Systems: Servo motors use sensors (such as encoders) to provide feedback to the motor controller, allowing it to adjust its speed, position, and torque accordingly.
Torque Control: Servo motors are appropriate for applications requiring controlled and smooth motion because of their ability to provide high torque at a variety of speeds.
Efficiency: Servo motors are energy-efficient and can handle a range of loads and speeds, making them ideal for continuous, high-performance operations in CNC machines.
Types of Servo Motors in CNC Machines

AC Servo Motors
AC servo motors are among the most common types used in modern CNC machines. When great torque, speed, and efficiency are needed, they are usually utilized. They are powered by alternating current (AC). AC servo motors are very dependable for CNC machining applications because they use feedback mechanisms to precisely control the motor shaft’s position and speed.
Advantages of AC Servo Motors:
- High torque and speed
- Low maintenance due to absence of brushes
- Higher efficiency than DC motors
- Longer lifespan
DC Servo Motors
DC servo motors operate using direct current (DC) and are typically used in older CNC machines or for applications where high-speed performance is not as critical. While DC servo motors offer good control, they require more maintenance due to the presence of brushes that wear out over time.
Advantages of DC Servo Motors:
- Simple control systems
- Good torque at low speeds
- Less complex feedback systems
However, DC servo motors are being gradually replaced by AC motors in modern CNC machines due to their higher efficiency and lower maintenance needs.
Brushless DC (BLDC) Servo Motors
BLDC motors are perfect for high-performance applications since they don’t have brushes, which lessens mechanical wear and tear.
Advantages of BLDC Servo Motors:
- Higher efficiency and longer life
- Smooth operation due to absence of brushes
- Lower maintenance costs
- Superior performance at high speeds
Disadvantages: The primary drawback of BLDC motors is that they require more complex control systems, which can increase the cost of the CNC machine.
Comparison of Servo Motor Types
| Feature | AC Servo Motor | DC Servo Motor | Brushless DC Motor (BLDC) |
| Efficiency | High | Moderate | Very High |
| Torque Control | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Maintenance | Low (no brushes) | High (brush wear) | Very Low (no brushes) |
| Speed Range | Wide | Moderate | Very Wide |
| Application | Most modern CNC machines | Older or low-speed machines | High-performance CNC machines |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Moderate | High |
Role of Servo Motors in CNC Machines
Servo motors are essential for managing the axis movement of CNC machines. This is an explanation of their roles in a CNC system:
Precision Control
CNC machines require highly accurate control over their movement to ensure that each part is manufactured to exact specifications. Servo motors provide this precision by adjusting their rotation based on real-time feedback from sensors. This closed-loop system ensures that the machine follows the programmed path with high accuracy, avoiding errors that could lead to defective parts.
Dynamic Response
CNC machines are used for high-speed operations, where the tool or workpiece needs to accelerate, decelerate, and change direction quickly. Servo motors are capable of providing dynamic responses, making them ideal for CNC machines that require fast, smooth movements without sacrificing accuracy.
Continuous Motion
Unlike stepper motors, which move in discrete steps, custom servo motors can provide continuous, smooth motion. This is critical in applications where continuous motion is required for processes such as drilling, milling, and turning.
Feedback Loop
A servo motor system’s feedback loop continuously checks the motor’s position and speed and makes necessary adjustments. This ensures that the CNC machine stays on track and that any deviation from the programmed path is corrected in real time, providing unmatched accuracy in manufacturing.
Benefits of Using Servo Motors in CNC Machines
Using servo motors in CNC machines offers several key advantages:
Increased Accuracy and Precision
The ability of servo motors to adjust their position and speed in real-time allows CNC machines to achieve extreme precision. This ensures that parts are manufactured exactly according to specifications, reducing the need for rework and minimizing errors.
Improved Speed and Efficiency
Servo motors can operate at higher speeds while maintaining precision, improving the overall throughput of CNC machines. They can also handle varying loads efficiently, ensuring that production cycles are completed faster.
Energy Efficiency
Servo motors, particularly brushless DC motors, are energy-efficient due to their ability to only draw the amount of power required for the task. For users of CNC machines, this lowers energy consumption and operating expenses.
Reduced Wear and Tear
Because brushless servo motors do not require brushes, there is less mechanical wear and tear, which results in lower maintenance costs and a longer lifespan for CNC machines.
Enhanced Performance in Complex Operations
Servo motors can control multiple axes simultaneously, which is particularly beneficial for multi-axis CNC machines that need to perform complex operations. Their ability to provide smooth, coordinated movements is essential for operations such as 5-axis milling.

How to Select the Right Servo Motor for Your CNC Machine
Selecting the right servo motor for a CNC machine depends on several factors, including the machine’s application, load requirements, speed, and precision needs. Here are some considerations when choosing a servo motor for CNC:
Torque and Speed Requirements
The size and power of the servo motor should match the torque and speed requirements of the CNC machine. For instance, larger CNC machines that require heavy-duty work will need more powerful motors to provide sufficient torque and speed.
Feedback Type
The feedback system (encoder or resolver) should be compatible with the control system of the CNC machine. High-resolution encoders provide more precise feedback, which is crucial for high-precision applications.
Voltage and Power
The servo motor’s voltage and power ratings should match the CNC machine’s power supply. Proper alignment ensures optimal performance and avoids overloading the system.
Control Compatibility
Servo motors require specific controllers to regulate their speed, position, and torque. For smooth integration and operation, make sure the chosen motor is compatible with the CNC machine’s controller.
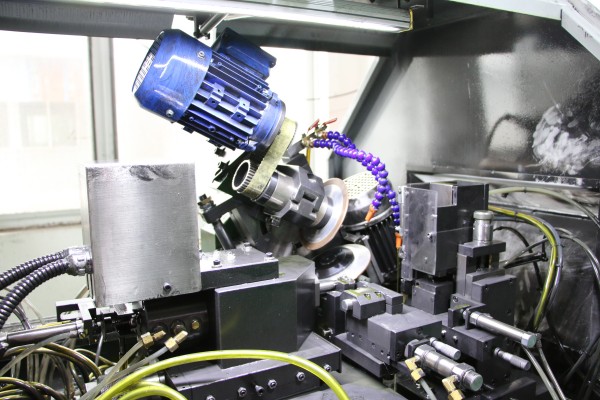
Applications of Servo Motors in CNC Machines
- 3-Axis CNC Milling Machines: For extremely precise drilling, contouring, and cutting of parts.
- 5-Axis CNC Machining Centers: For complex, multi-directional machining tasks like aerospace and automotive parts manufacturing.
- CNC Lathes: For turning operations with precise control of rotational speed and positioning.
- CNC Plasma Cutters: To quickly and accurately cut metal and other materials.
- CNC Routers: For wood, plastic, and metal cutting, where precision and speed are required.
Because they power the high-precision movements needed for contemporary manufacturing, servo motors are a crucial part of CNC machines. By providing accurate, smooth, and efficient motion control, servo motors enable CNC machines to perform complex operations that are vital to industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Whether using AC servo motors, DC motors, or Brushless DC (BLDC) motors, selecting the right motor from a reliable servo motor manufacturer is critical to achieving optimal performance and efficiency.