What is a Slotted Brushless DC Motor?
An electric motor that runs without brushes for commutation is known as a slotted brushless DC (BLDC) motor. Rather, the current flow via the motor windings is controlled by electronic controllers. The term “slotted” refers to the design of the stator, which has slots to house the windings.
Working Principle:
Magnetic Field Generation:
The electronic controller supplies current to the windings in a precise sequence, creating a rotating magnetic field in the stator.
Rotor Interaction:
The revolving magnetic field produced by the stator windings has an influence on the permanent magnets located on the rotor.
The torque generated by the magnetic forces between the rotor’s magnets and the stator’s spinning field causes the rotor to rotate.
Commutation:
In BLDC motors, commutation is accomplished electronically, in contrast to brushed motors.
Sensors (such as Hall effect sensors) or sensorless control methods determine the rotor position, allowing the controller to switch the current in the windings at the right times to maintain rotation.
Continuous Rotation:
The controller continuously adjusts the current in the windings, ensuring a smooth and efficient rotation of the rotor.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|
|
What is a Slotless Brushless DC Motor?
A slotless brushless DC (BLDC) motor is a type of BLDC motor that eliminates the slots found in the stator of traditional slotted BLDC motors. In a slotless design, the windings are placed directly on the stator core surface, which is typically made of laminated steel.
Working Principle:
Magnetic Field Generation:
The electronic controller supplies current to the windings, creating a rotating magnetic field in the stator.
Rotor Interaction:
The rotor spins because of the torque produced by the interaction between the whirling magnetic field produced by the stator windings and the rotor’s permanent magnets.
Commutation:
To maintain continuous rotation, electronic commutation is employed to switch the current in the windings dependent on the position of the rotor.
Pros and Cons
Pros | Cons |
|
|
What’s the difference between Slotted Brushless DC Motor and Slotless Brushless DC Motor?
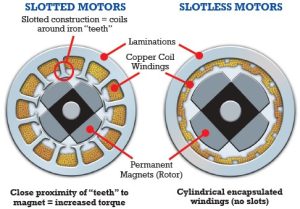
Stator Design:
- Slotted BLDC Motor:
- Features a stator with slots where the windings are placed.
- The slots help in holding the windings and contribute to the formation of a cogging torque due to the slot geometry.
- Slotless BLDC Motor:
- Has a smooth stator without slots, with windings placed directly on the core surface.
- Eliminates cogging torque, resulting in smoother operation.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI):
- Slotted BLDC Motor:
- The presence of slots can cause variations in the magnetic field, leading to higher EMI.
- Slotless BLDC Motor:
- The smooth stator surface reduces variations in the magnetic field, leading to lower EMI.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost:
- Slotted BLDC Motor:
- Easier and less expensive to manufacture due to the straightforward placement of windings in the slots.
- Slotless BLDC Motor:
- More complex and expensive to manufacture due to the precision required in placing windings on the smooth core surface and managing thermal dissipation effectively.
| Aspect | Slotted Brushless DC Motor | Slotless Brushless DC Motor |
| Construction | Has slots in the stator | Smooth stator |
| Torque Ripple | Higher torque ripple | Lower torque ripple |
| Efficiency | lower efficiency | Higher efficiency |
| Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) | Higher EMI levels | Lower EMI levels |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Simpler, lower cost | More complex, higher cost |
| Torque Density | Higher torque density | Lower torque density |
| Applications | power tools, industrial machinery | medical devices, precision instruments |
How to choose slotted brushless DC motors and slotless brushless DC motors?
A number of criteria, including as economic concerns, environmental factors, and performance requirements, must be taken into account when choosing the right brushless DC (BLDC) motor for your application.
Application Requirements
Torque Ripple
- Slotted: If your application can tolerate higher torque ripple (e.g., power tools, industrial machinery), a slotted motor may be suitable.
- Slotless: For applications requiring smooth operation with minimal torque ripple (e.g., medical devices, precision instruments), choose a slotless motor.
Efficiency
- Slotted: Suitable for applications where efficiency is less critical.
- Slotless: Ideal for applications requiring high efficiency due to reduced losses.
Torque Density
- Slotted: Offers higher torque density, making it suitable for applications requiring more torque in a compact size.
- Slotless: Suitable for applications where lower torque density is acceptable.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
- Slotted: Higher EMI, suitable for environments where EMI is not a major concern.
- Slotless: Lower EMI, making it ideal for sensitive applications like medical and communication equipment.
Thermal Management
- Slotted: Better heat dissipation due to the presence of slots in the stator.
- Slotless: This may require additional cooling mechanisms due to more challenging heat dissipation.
Cost and Manufacturing
- Slotted: Generally less expensive to manufacture and suitable for budget-conscious projects.
- Slotless: Higher initial cost due to more complex manufacturing but may offer long-term cost savings through improved efficiency and lower EMI.
Environmental Conditions
- Slotted: Suitable for rugged environments where robust construction is needed.
- Slotless: More suitable for clean environments where precision and smooth operation are critical.
Conclusion
By evaluating these factors based on your specific application needs, you can make an informed decision on whether a slotted or slotless brushless DC motor is the best fit for your project.
If you still don’t know how to choose, please contact us and we will arrange a one-to-one service for you.